We have previously blogged about the risk and challenges in Securing AWS Temporary Tokens.
In this blog, we will take a fresh look from the MITRE Att&ck chain viewpoint, in order to highlight new insights and specific cloud techniques used by adversaries, in an effort to help users be more effective in detecting, mitigating, and preventing different but similar attacks.
Recap: Securing AWS Temporary Tokens
Let’s summarize the challenges with temporary tokens and the common mitigation steps, before we contrast this with what we can glean from an Att&ck analysis.
Here is the original attack scenario:
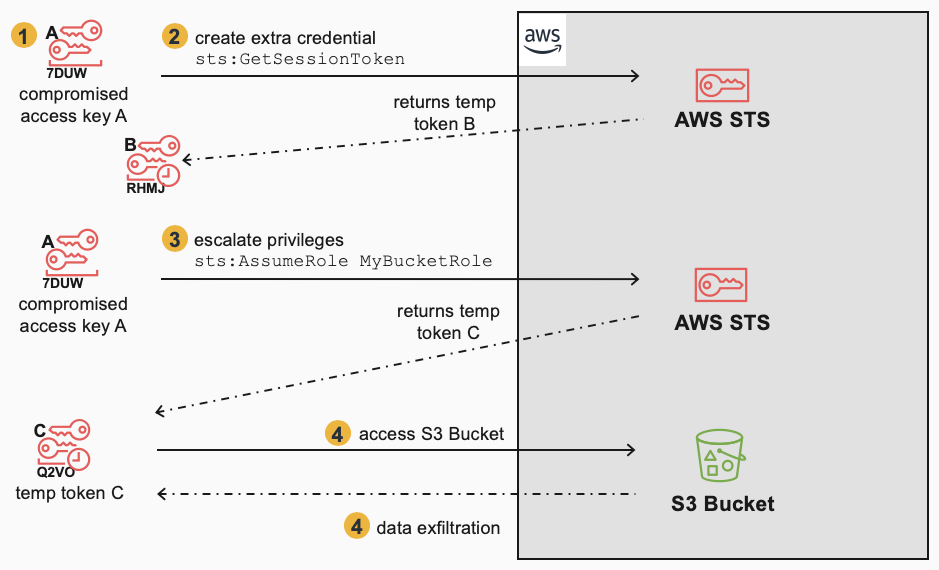
The key steps are:
- A permanent Access Key A is compromised
- Key A is used immediately to generate an extra credential i.e. Temporary Token B (for backdoor purposes and obfuscation)
- Key A is used to escalate privileges via AssumeRole, which returns Temporary Token C
- Temporary Token C is then used to access an S3 Bucket
- Temporary Token C is used to exfiltrate data from the S3 Bucket
When mitigating this scenario, the defender first deleted/inactivated Access Key A, then also had to remember to “revoke” Temporary Token C. Revocation in this case meant using a specific role policy to deny all API calls by Temporary Token C based on its creation time.
However, this did not remove the adversary’s access, as there was still the existing Temporary Token B, which could also be used to escalate privileges and generate more temporary tokens (D) in order to continue access to the S3 Bucket:
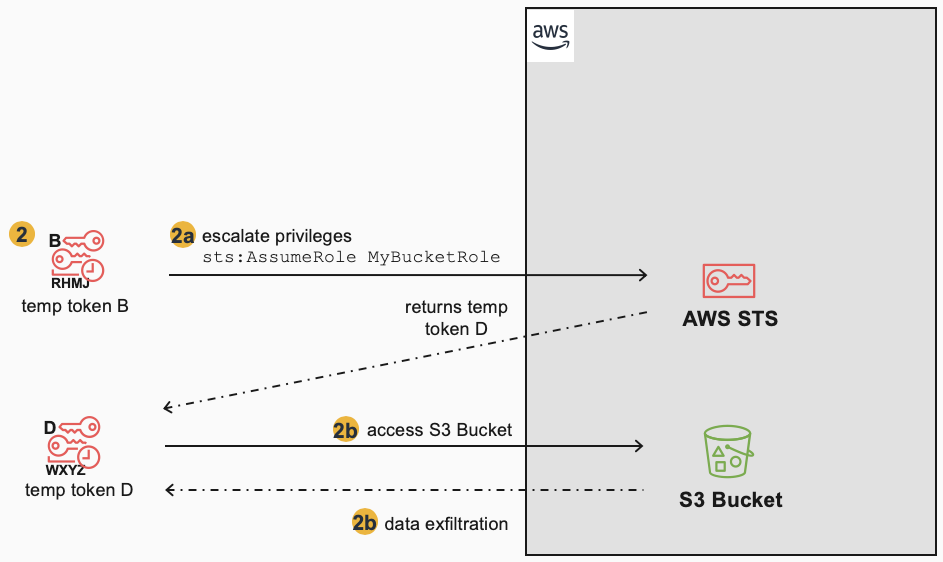
To completely mitigate the situation, the Temporary Token D must be “revoked” in the same manner as Temporary Token C (using the role policy based on creation time). However, this mitigation approach doesn’t work for Temporary Token B, which was created not by AssumeRole, but by GetSessionToken. In this case, the only way to mitigate/remove Temporary Token B is to delete the IAM user that “owns” it (i.e. the same IAM user that had the compromised Key A) or to restrict that IAM user’s permissions.
These mitigation steps and their differences can be summarized here:
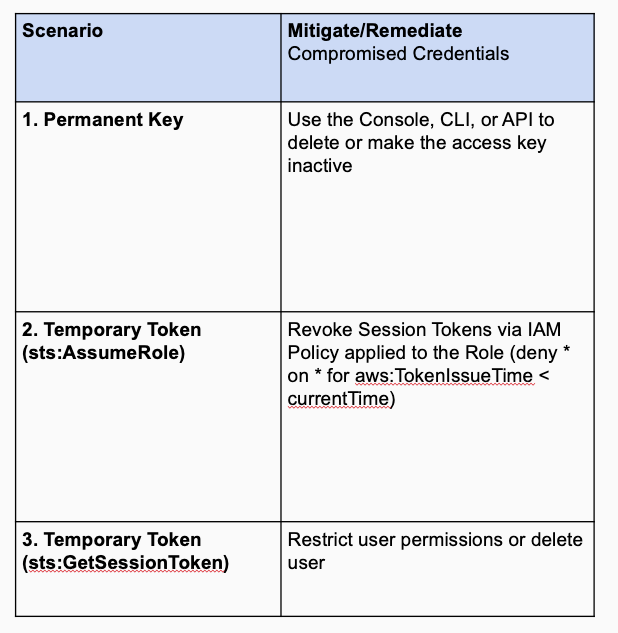
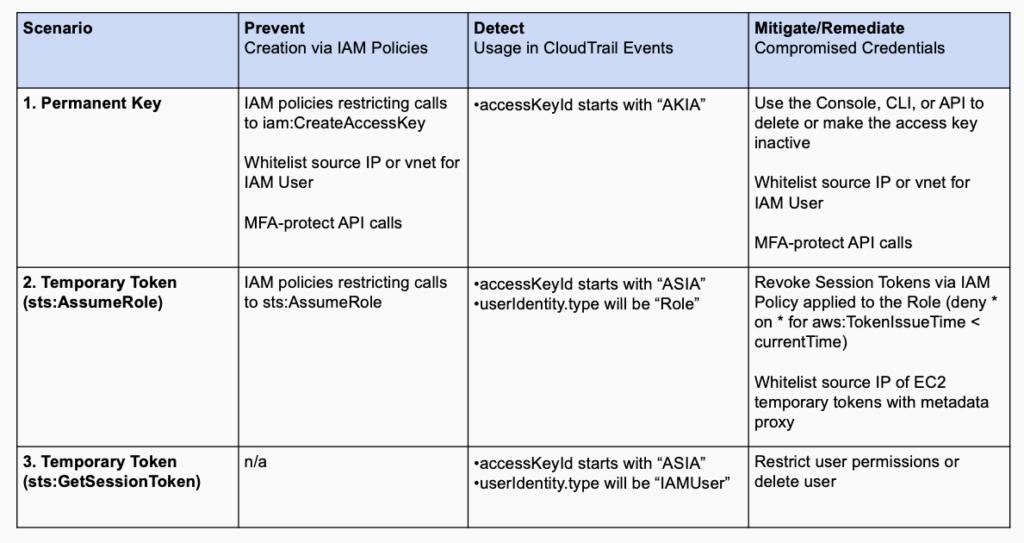
This table reflects an incident-focus in dealing with temporary tokens. When taking a larger viewpoint, it’d be reasonable to think about a more complete set of preventative, detection, and mitigation measures:
MITRE Att&ck
Let’s now look at the scenario from the Att&ck viewpoint and see what new insights we have. The original attack scenario has been reorganized in more of an attack chain flow along with MITRE references for the tactics/techniques involved:
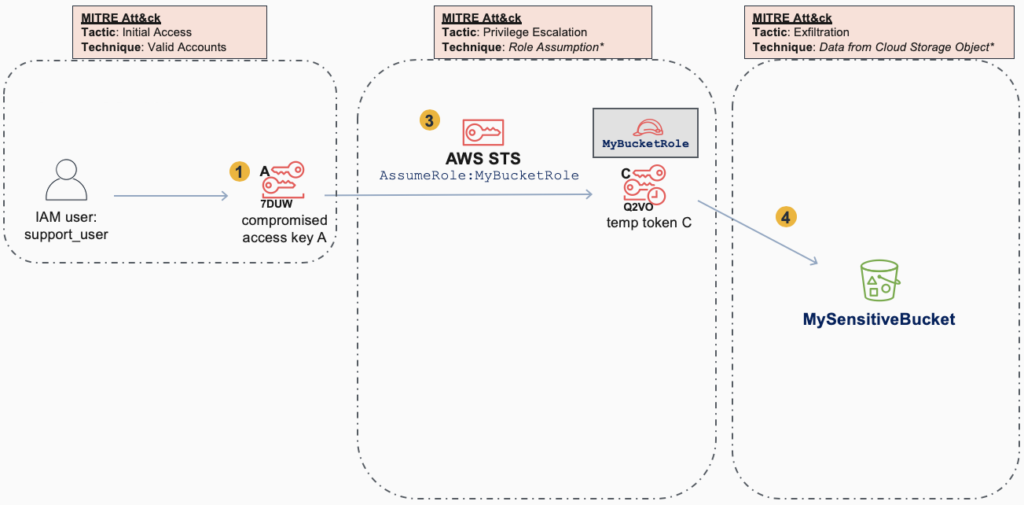
Notice how this primary attack scenario reflects what a defender might be focused on if they were in the middle of an incident. These would be the primary artifacts seen when tracing back from data exfiltration events to the originating credentials. Role Assumption is a good example of a new technique that isn’t yet in the Privilege Escalation tactic in Att&ck, but is common in cloud attacks. Netskope is working to identify additional techniques such as this, so that defensive measures can be specific and clear.
This Att&ck reorganization is easier to understand and also allows a defender to mine the Att&ck knowledge base for ways to detect and mitigate this attack at each step.
Let’s now look at the secondary attack:
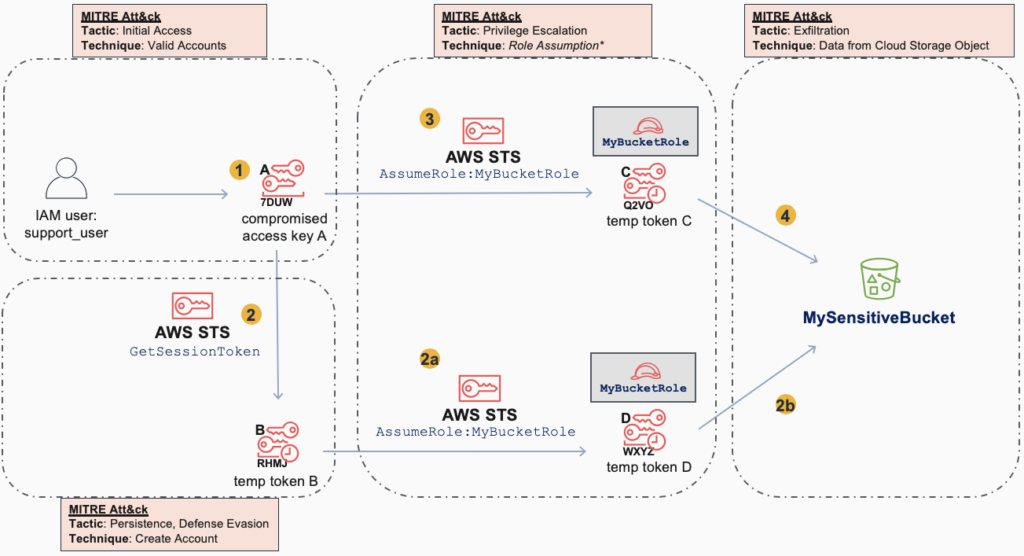
Here, it is more obvious, that Temporary Token B is part of an attempt at Persistence (backdoor access) and possibly Defense Evasion, and it’s clearer how it provides the same access to the S3 Bucket.
Here’s a summary of the tactics and techniques in the attack:
| (1) A permanent Access Key A is compromised Tactics: Initial Access Techniques: Valid Accounts Mitigations: User Training, Network Segmentation, Multi-factor Authentication IP allow list credential use, multi-factor authentication, and user training can be effective measures to help prevent and mitigate compromised access keys. |
| (2) Key A is used to generate an extra credential (create Temporary Token B using GetSessionToken) Tactics: Persistence, Defense Evasion Techniques: Redundant Access Mitigations: n/a GetSessionToken calls cannot be prevented, as they are part of authentication. Mitigation techniques involve early detection by looking for calls to GetSessionToken in CloudTrail events. |
| (3,2a) Key A or Temporary Token B is used to escalate privileges (create Temporary Token C or D using AssumeRole) Tactics: Privilege Escalation Techniques (proposed): Role Assumption and User Impersonation Mitigations: Multi-factor Authentication, Privileged Account Management To mitigate compromised temporary tokens generated by AssumeRole, use a revoke session token policy with a condition based on the creation time of the token. Requiring multi-factor authentication for manual calls to AssumeRole is also a good measure. Ensuring minimal access rights are granted to PassRole and AssumeRole can also mitigate problems. In some specific cases, such as EC2 instance creation, the AssumeRole temporary token can be allow listed to the EC2 instance IP using a metadata proxy, helping reduce the chances for abuse when the tokens are compromised. |
| (4,2b) Temporary Token C or D is used to access/exfiltrate data from an S3 Bucket Tactics: Exfiltration Techniques: Data from Cloud Storage Object Mitigations: Audit, Encrypt Sensitive Information, Multi-factor Authentication, Restrict File and Directory Permissions, User Account Management To mitigate unauthorized access to S3 Buckets, ensure S3 bucket permissions are not public, try to simplify bucket/object policies, and monitor event logs for suspicious API access. Multi-factor authentication in a resource-based policy can help ensure manual access is authorized. Finally, encrypt sensitive data, so that impact from loss of data is minimized. |
By classifying the Att&ck techniques and tactics used, we can see commonality and differences in the original and secondary attack scenarios. Namely, step 2 involved a different API call to generate a temporary token (GetSessionToken) vs. the assumption of a role (AssumeRole). Further, the escalation of privileges and data exfiltration in both scenarios are the same. This allows us to focus on what is different in the mitigations, detections, and preventions for temporary token creation (GetSessionToken vs AssumeRole). Additionally, we can look to reuse/leverage common mitigations, detections, and preventions for the escalation of privilege and exfiltration (AssumeRole and S3 bucket access).
Detection, Mitigation, Prevention
Let’s dive deeper into the analysis by overlaying not only common detection, mitigation, and prevention measures from Att&ck, but also other measures, such as best practices or the defender’s own policies. We get this view:
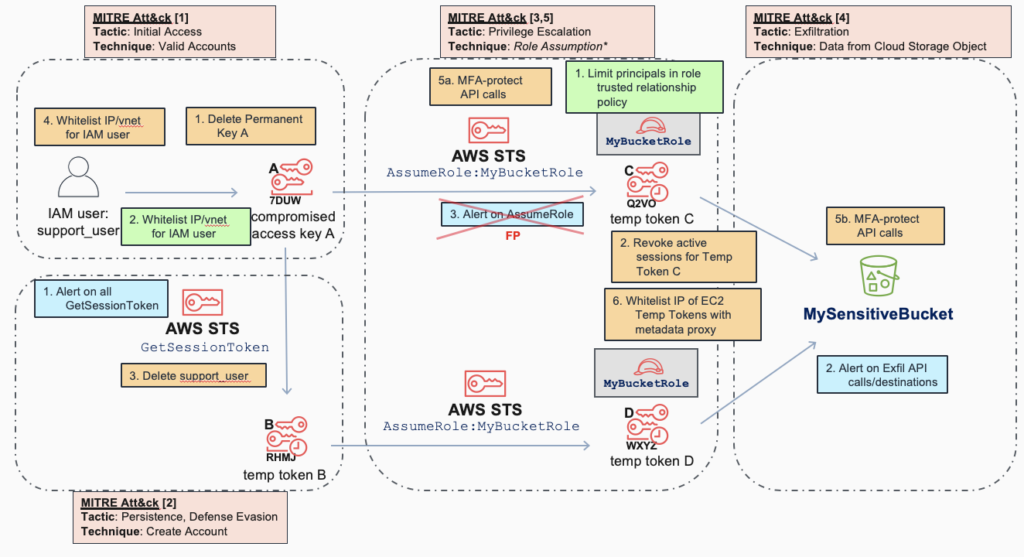
The advantages of this Att&ck view are:
- Defenders can be more comprehensive along all of the attack chain not just with mitigations but with better detection and prevention.
- Defenders can reuse knowledge as captured in Att&ck for common detections or mitigations, to make planning, implementation, and response quicker and more standardized.
- Defenders can also analyze measures as to their efficacy (potential for FP or FN). An example of this is that simple alerting on AssumeRole is too noisy (FP) as it is called by many services when passing roles during invocation (e.g. EC2, Lambdas), so #3 (blue) above was determined to not be a good detection measure.
The analysis from the Att&ck diagram above can be detailed in a structured table:
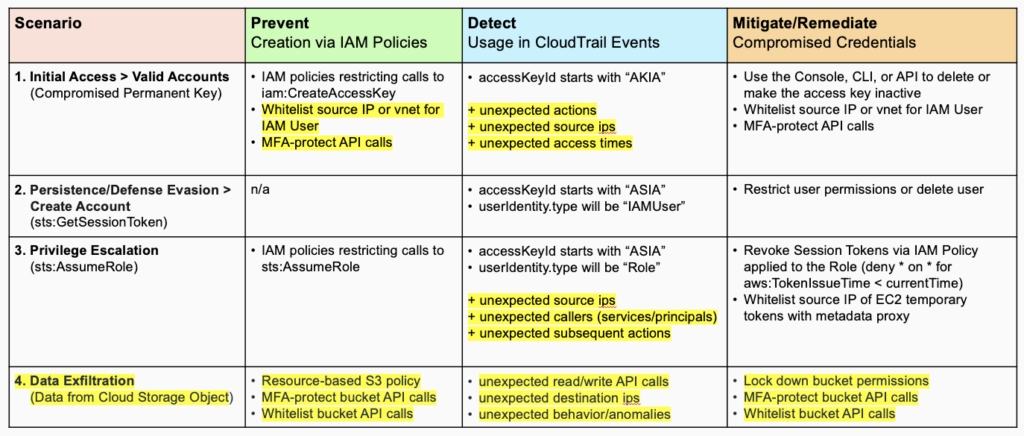
The highlighted (yellow) measures are some of the points that either weren’t obvious or weren’t a priority from the first analysis done.
Conclusion
Taking an Att&ck viewpoint on incidents or attack vectors can be useful for several reasons:
- It provides a common, more repeatable framework for analysis, reducing tribal knowledge or inconsistent approaches
- It allows for easier reuse of defensive measures for mitigation, detection, and prevention
- It allows for a more comprehensive checklist by making it clear what each step of the attack chain is, making it less likely to forget to analyze steps
- It can highlight new cloud techniques being used by adversaries (as the cloud providers continue to add services and APIs). In this case, Role Assumption is a common technique used that is more specific than just using Valid Accounts within the Privilege Escalation tactic, and it’s worth calling this out so the community can share specific practices for mitigating, detecting, and preventing abuse via this technique
By looking at the original attack scenarios in several ways from an Att&ck viewpoint, first by classified tactic/technique, then by wider-ranging analysis in a flow diagram, we are able to better evaluate the attack scenario and effective measures for detection, mitigation, and prevention.




 Atrás
Atrás 





















 Lea el blog
Lea el blog