The advent of cloud applications led to a new generation of phishing attacks (named OAuth phishing or consent phishing) where, rather than stealing the user credentials, threat actors aim to obtain an authorization token via a rogue cloud app that allows them to perform harmful activities on the victim’s cloud environment. These activities include: reading emails, sending emails on behalf of the victim itself, reading the calendar, changing profile and email settings, and many others permissions that can be exploited to steal confidential information from the target.
The so-called user experience is similar to a traditional phishing attack. The victim receives a malicious link, for example via a spear phishing email, but instead of being presented with a form mimicking a legitimate app eager to steal their credentials, they are presented with an authentication page where a seemingly legitimate cloud app asks to access their cloud environment with specific permissions on behalf of the user, permissions that the victims do not double check and end up delivering attackers the keys of the kingdom Multi-factor authentication does not help to mitigate this attack, since the user must authenticate to the target app to provide consent to the malicious application. Then once the authorization token is issued, the only way to remediate is to delete the malicious app from the target environment or, in other terms, revoke the token.
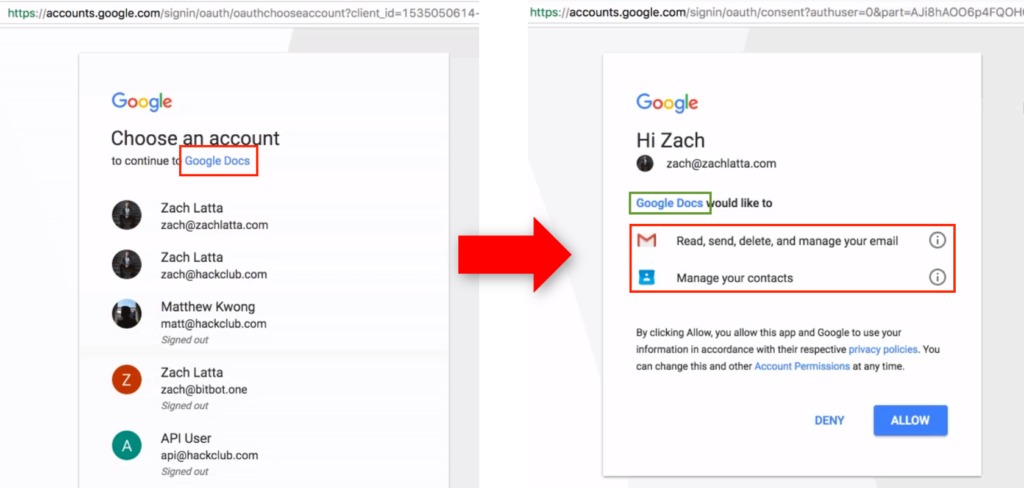
Threat actors have been exploiting this technique since at least 2017 for both opportunistic and targeted campaigns: APT 28 (also known as Pawn Storm) is the first known example of a state-sponsored threat actor exploiting OAuth phishing since 2017. But the risks of this attack were almost completely unknown to the wider audience, until May 3rd of the same year, when a massive OAuth worm hit more than one million Google Workspace users (and yes, it was called G Suite back then).
Since then, there have been multiple examples of campaigns carried out via OAuth phishing, and the risks connected with third-party application access to corporate data are a reality, and will also be the topic of a presentation of our Netskope Threat Labs at the forthcoming RSA Conference by our top-rated speaker Jenko Hwong.
In the latest occurrence, Microsoft and Proofpoint have just taken down a network of fraudulent, verified Microsoft Partner Network accounts exploited to create malicious OAuth applications with the purpose to infiltrate the cloud environments of corporate users in the UK and Ireland and steal sensitive information.
The campaign occurred between December 6 and December 27, 2022, and the threat actors impersonated credible publishers to become verified themselves, and provide even better legitimacy to the malicious OAuth apps. According to Microsoft, the rogue apps were used to steal customers’ emails, but according to Proofpoint, the reality is unsurprisingly worse since the app’s permissions could have allowed the attackers to access calendars and meeting information and modify user permissions.
How Netskope mitigates the risk of consent phishing
Netskope SSPM (SaaS Security Posture Management) continuously monitors and enforces SaaS security settings, policies, and best practices to reduce security and compliance risks, helping organizations to detect rogue applications with harmful permissions and enforce the corresponding remediation actions. Among the entities that can be monitored for a Microsoft 365 environment, there are also the OAuth permission grants to third-party apps (entity OAuth2PermissionGrant), so that organizations can be alerted if an OAuth app obtains permissions considered harmful and too intrusive. As noted earlier, once a user falls into the trap of OAuth phishing, the only possibility is to revoke the authorization token and remove the application, and Netskope SSPM can certainly identify malicious OAuth apps and provide the organization with actionable information to remediate the threat.
For example a rule that verifies that the OAuth permissions granted to third-party apps will not modify app role assignments, is part of the predefined profiles:
- CSA-CCM-4.0– CSA Cloud Controls Matrix
- GDPR-2016-679– General Data Protection Regulation 2016/679
- HIPAA-1996– Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996
- ISO-27002-2013– ISO/IEC 27002:2013
- NIST-CSF-1.1– NIST Cybersecurity Framework
- NIST-800-53-4– NIST SP 800-53 Rev. 4
- PCI-DSS-3.0– PCI Data Security Standard v3.0
- AICPA-SOC-TSC-2017– AICPA SOC2 2017 Trust Services Criteria for Security, Availability, Processing Integrity, Confidentiality, and Privacy
However it is also possible to create custom rules that check for specific scopes considered harmful or non-compliant with the internal policies.
Stay safe!




 Voltar
Voltar 





















 Leia o Blog
Leia o Blog