Netskope Threat Research Labs detected several targeted themed attacks across 42 customer instances mostly in the banking and finance sector. The threat actors involved in these attacks used the App Engine Google Cloud computing platform (GCP) to deliver malware via PDF decoys. After further research, we confirmed evidence of these attacks targeting governments and financial firms worldwide. Several decoys were likely related to an infamous threat actor group named ‘Cobalt Strike’.
The attacks were carried out by abusing the GCP URL redirection in PDF decoys and redirecting to the malicious URL hosting the malicious payload. This targeted attack is more convincing than the traditional attacks because the URL hosting the malware points the host URL to Google App Engine, thus making the victim believe the file is delivered from a trusted source like Google.
This post describes our discovery and analysis of the Google App Engine URL Redirection abuse, the threat actor responsible, and the malware abusing this feature. We conclude with some recommendations to help protect and remediate such threats.
Netskope Detection
Netskope Advanced Threat Protection detects the targeted decoy we identified as PDF_Phish.Gen.
Disclosure
Netskope reported this abuse to Google on 10 January 2019. The open redirector exists by design.
Discovery
Early this year, Netskope’s telemetry identified common detections across 42 customers in the banking and finance sector. All these were eml files that carried an .eml extension and had the same detection name, triggering alerts in our Outbreak Detection Systems. After investigation, we confirmed that the detections were triggered in the attachments of the eml files.
Leveraging our Netskope Discovery and Netskope Active Introspection Alerts platforms, we discovered these attacks were abusing Google App Engine on the Google Cloud Platform (GCP) as a bait to deliver malware.
PDF Decoys – Delivery
The PDF decoys traditionally arrive as email attachments to victims. The emails are crafted to contain legitimate content and deliver the malware from allow listed sources. Often, such attachments are saved to cloud storage services, like Google Drive. Sharing these documents with other users can result in the occurrence of a secondary propagation vector like the CloudPhishing Fan-out Effect. In this case, the email file containing the decoy document was detected by Advanced Threat Protection and the potential fan-out was prevented.
GCP App Engine URL Redirection – Decoys
This targeted attack is more convincing than the traditional attacks because the decoy deceives the victim with a GoogleApp Engine URL which is abused to redirect the victim to the malware. As the payload seems to be originating from a trusted source, the chance of falling victim to such attacks is very likely.
The themed PDF decoys we observed using GCP App Engine URL Redirection is shown in Figure 1.
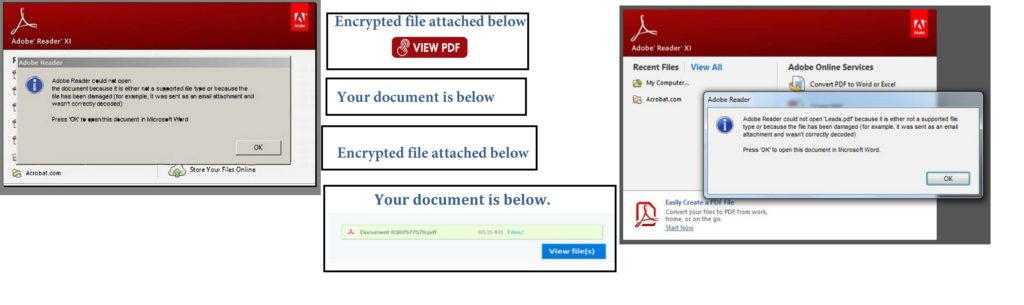
Most of the PDF’s we observed were created using Adobe Acrobat 18.0. They contained the malicious URL in a compressed form in the PDF stream using Flat Decode (Filter/FlateDecode). Similarly, all the decoys used HTTPS URLs for delivering the payload.
GCP App Engine URL Redirection – Overview
The URL redirection case with Google App Engine falls under the category of Unvalidated Redirects and Forwards as per the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP).
Some of the URLs we observed from the PDF decoys using this technique are shown below
- https://appengine.google[.]com/_ah/logout?continue=https%3A%2F%2Ftransef[.]biz%2FDoc102018.doc
- https://appengine.google[.]com/_ah/logout?continue=https%3A%2F%2Fswptransaction-scan2034.s3.ca-central-1.amazonaws[.]com%2FDoc102018.doc
For a better understanding and illustration, we have taken the below URL as an example
- https://appengine.google[.]com/_ah/logout?continue=https%3A%2F%2Ftransef[.]biz%2FDoc102018.doc
The packet capture illustrating this activity is shown in Figure 2.
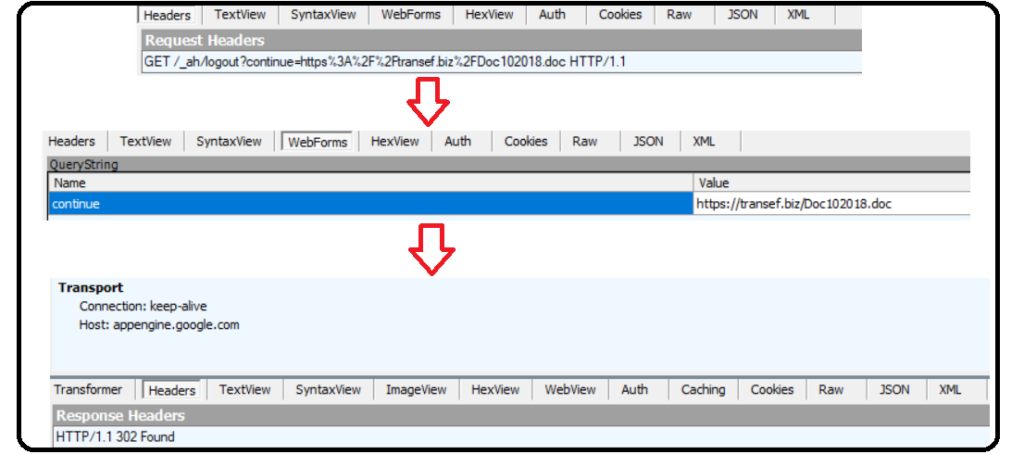
Figure 2 illustrates that once the URL is accessed, the user is logged out from appengine.google.com and a response status code ‘302’ is generated for URL redirection. As this action gets executed, the user is inturn redirected to google.com/url using the query “?continue=”. Using this redirection logic, the destination landing page is reached, and in this case, Doc102018.doc is downloaded to the victim’s machine.
Using the same logic in the query, we tried the same approach with GCP App Engine URL as follows:
- https://accounts.google.com/Logout?continue=https://appengine.google.com/_ah/logout?continue=https%3A%2F%2Ftransef[.]biz%2FDoc102018.doc
- https://google.com/accounts/Logout?continue=https://appengine.google.com/_ah/logout?continue=https%3A%2F%2Ftransef[.]biz%2FDoc102018.doc
In all these cases, the GCP App Engine application successfully validated the redirection and delivered the payload to the victims machine.
Since the appended URL is an unvalidated redirect, the threat actors abused this feature by redirecting a victim to a malicious appended URL hosting the malicious payload.
PDF Decoys – Default Allow policy
Generally, PDF readers prompt a security warning to the user when the document connects to a website. Once “remember this action for this site” is checked for a domain, this feature allows any URL within the domain without any prompt.
The activity illustrating this action is shown in Figure 3.
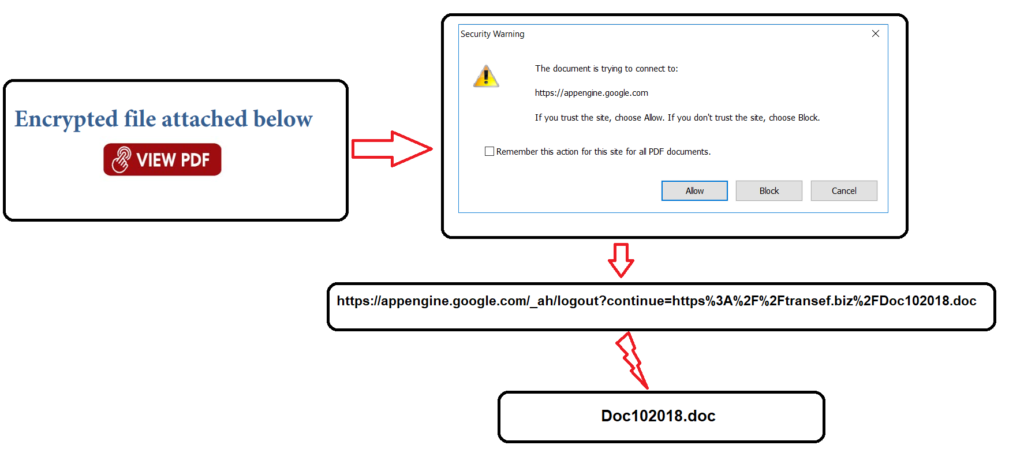
By taking advantage of the “default allow” action in popular PDF readers, the attacker can easily deploy multiple attacks without getting the security warning after the first alert. It is also possible that appengine.google.com is allow listed by the administrators for legitimate reasons. It also only warns the user that it is trying to connect to appengine.google.com, which looks benign at face value.
Malware using GCP URL Redirection
All the PDFs involved in this attack downloaded Microsoft Word documents with obfuscated macro code or PDF documents as the second stage payload.
The PDF decoy detected in our customer instances downloaded a word document named “Doc102018.doc” containing obfuscated macro code. This document was downloaded from the URL https://transef[.]biz.
On execution, the victim is presented with a message to enable editing and content mode to view the document as shown in Figure 4.

On enabling the option, the macro gets executed and downloads another stage payload from transef[.]biz/fr.txt. The stage payloads are often used by threat actors to ensure a smoother transition and to make an attack harder to detect, investigate and mitigate
fr.txt is detonated using Microsoft Connection Manager Profile Installer (csmtp.exe) from the location, %Appdata%\Roaming\Microsoft\26117.txt as an INF file shown in Figure 5.
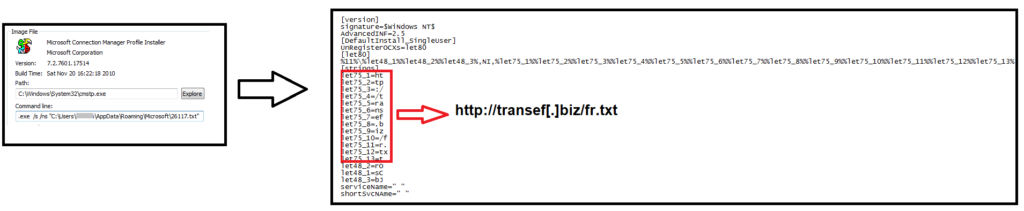
This technique resembles to the “Squiblydoo” technique, detailed in our previous research of ShortJSRAT. Squiblydoo is a technique wherein malicious scriptlets are loaded using native Windows applications. This bypasses application allow listing solutions like Windows Applocker, which allow only approved applications to load and execute.
At the time of analysis, the next stage payload “fr.txt” was down and not serving any payload. Though the payload was down, we leveraged our Netskope Threat Intelligence to attribute these attacks to an infamous threat actor group named ‘Cobalt Strike’, detailed in an research article by Cisco Talos.
The ‘Cobalt Strike group’ has a reputation of targeting financial and Banking firms using several Tactics, Techniques and Procedures (TTPs), using malware like the high-profile Carbanak malware. This group is also known to heavily use a the software Cobalt Strike in its arsenal. The Cobalt Strike software is a white-hat tool for performing security assessments that replicates the tactics and techniques of an advanced adversary in a network.
Though the mastermind of the group was arrested on March 26th, 2018 by Europol, there are still some targeted attacks executed by the group. Based on the timeline of the emails sent to the potential targets we expect the group to be actively carrying out attacks.
PDF Decoys – Emails and potential targets
Based on our threat intelligence research, more than 20 other banking, government and financial institutions were targeted with the same attack via phishing emails sent by the attackers posing as legitimate customers of those institutions
- Metrobank Philippines
- Prime Commercial Bank Ltd, Nepal
- BancNet Online
- Banque du Caire, or “Bank of Cairo”
- Itaú International Investment
- Ministry of External Affairs, India
- YapıKredi
- Bank of Alexandria
- OmniPay, Asia
- Bancosol
- Travelex foreign exchange business
- Standard Bank, South Africa
- MCB: Mauritius Commercial Bank
- Extraco Bank
- Bank Albilad
- Accuity
- SKB Bank, Russia
- RGS Bank, Russia
Some of the most commonly used email domains and email address by the threat actor are as follows
- pace.edu
- ulaval.ca
- metacase.eu
- ivywise.com
- ebf.eu.com
Although the emails were sent to the targets from the threat actor, there is a possibility that these email address might be a spoofed with a forged sender.
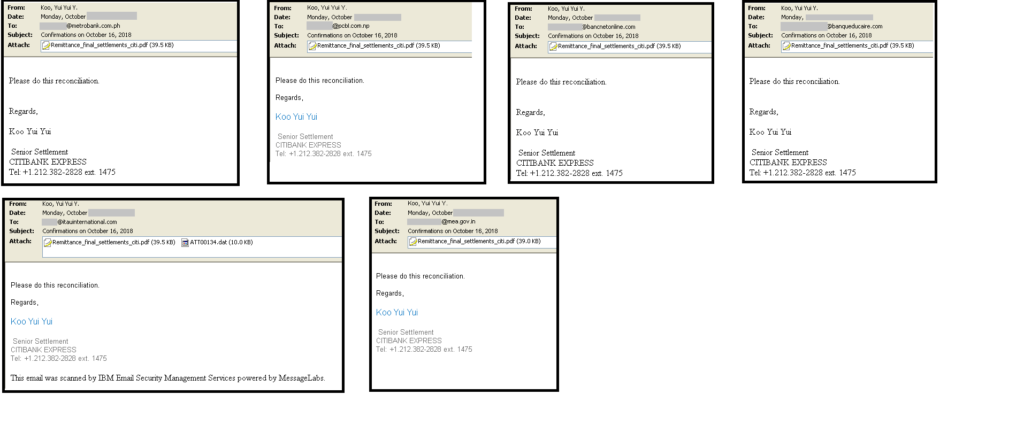
An example of emails sent from the email address [email protected], to a list of 6 potential targets as shown in Figure 6.
Conclusion
Our research initially started with the discovery of GCP URL abuse triggering detections across 42 customers in the banking and finance sector. Our in-house systems and Netskope Threat Intelligence Framework connected the dots and seamlessly aided us in tying the attacks to the infamous ‘Cobalt Strike’ threat actor group.
URL redirection mechanisms / features are widely used and abused by threat actors to deceive victims into believing the malicious file is being delivered from a trusted source. The usage of themed PDF decoys with enticing emails is a perfect choice since the payload seems to be originating from a trusted source and popular PDF viewers enable users to easily allow list domains.
Users can recognize URL redirection abuse by hovering the mouse over all hyperlinks before connecting to the URL. Enterprises should educate their users to recognize AWS, Azure, and GCP URLs, so they can discern malicious sites from official sites.
Netskope Advanced Threat Protection, with its unique cloud vantage point and multi-layered threat detection and remediation capabilities, offers customers a cloud scale platform that understands, and responds to such attacks, preventing them from spreading in your cloud environments.
Netskope Threat Research Labs will continue to monitor the developments of ‘Cobalt Strike’ threat actor group.
Recommendations
Netskope recommends the following to combat cloud-based phishing campaigns:
- Always check the domain of the link. Know the domains typically used when you login to sensitive services. Additionally, be able to identify common object store domains. This knowledge will help you differentiate between well-crafted phishing / malware sites and official sites.
- Deploy a real-time visibility and control solution to monitor activities across sanctioned and unsanctioned cloud accounts.
- Get comprehensive threat and malware detection for IaaS, SaaS, PaaS, and the web with real-time, multi-layered threat detection and remediation to prevent your organization from unknowingly spreading similar threats.
- Actively track usage of unsanctioned cloud apps and enforce DLP policies to control files and data entering and leaving your corporate environment
- Warn users against opening untrusted attachments, regardless of their extensions or filenames.
- Warn users to avoid executing any file unless they are very sure that they are benign.
- Un-check the option “Remember this action for this site for all PDF documents” in the PDF reader software, even if the site appears to be something legitimate, like appengine.google.com
- Hover your mouse over all hyperlinks to confirm them before clicking on the link.
- Actively track URL links added to the “Always Allow” list in PDF reader software
- Keep systems and antivirus updated with the latest releases and patches.




 Retour
Retour 





















 Lire le blog
Lire le blog